Trong kỳ thi IELTS Writing ngày 08/08/2024, thí sinh đã phải đối mặt với một thử thách thực sự khi đề bài yêu cầu phân tích một dạng bài kết hợp (mixed chart) giữa biểu đồ đường và biểu đồ cột ở Task 1.
Trong khi đó, Task 2 yêu cầu thí sinh nêu quan điểm cá nhân về ý kiến cho rằng người lao động cần được cho phép ít nhất bốn tuần nghỉ phép mỗi năm để cải thiện hiệu suất công việc. Bài viết này sẽ giúp thí sinh phân tích chi tiết và hướng dẫn cách tiếp cận đề thi này một cách hiệu quả, giúp thí sinh chuẩn bị tốt hơn cho kỳ thi IELTS của mình.
Hãy cùng xem xét đề thi Task 1 và Task 2 để hiểu rõ hơn về cách thực hiện bài viết này.
- Đề IELTS Writing task 1: The graph below shows the number of males and females studying different subjects and the total in 2012. Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features and make comparisons where relevant.
- Đề IELTS Writing task 2 thuộc dạng Agree or disagree với chủ đề Work: Employers should give their staff at least four weeks’ holiday per year to improve their job performance. To what extent do you agree or disagree?
Để nắm vững cách viết Task 1 và Task 2 trong phần Writing của IELTS, chúng ta sẽ tiến hành phân tích biểu đồ hỗn hợp trong Task 1 và đưa ra quan điểm cá nhân trong Task 2 bằng cách tham khảo các bài mẫu theo từng band điểm từ bài giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 08/08/2024.
1. IELTS Writing Task 1
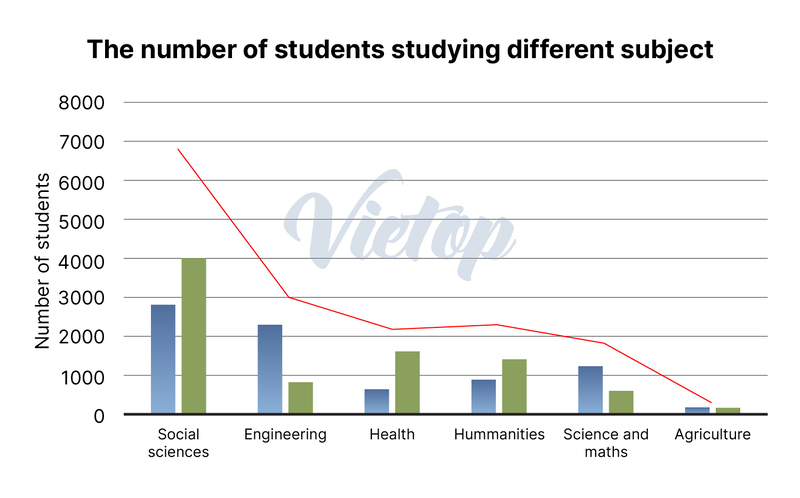
| The graph below shows the number of males and females studying different subjects and the total in 2012. Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features and make comparisons where relevant. |
| (Biểu đồ dưới đây cho thấy số lượng nam và nữ học các môn học khác nhau và tổng số sinh viên theo học vào năm 2012. Hãy tóm tắt thông tin bằng cách chọn lọc và báo cáo những đặc điểm chính, đồng thời so sánh khi cần thiết.) |
1.1. Bước 1: Phân tích đề
- Dạng biểu đồ: Biểu đồ kết hợp giữa biểu đồ cột và biểu đồ đường.
- Topic: Số lượng nam và nữ học các môn học khác nhau và tổng số sinh viên theo học.
- Place: Không đề cập.
- Number of factors: 6.
- Time: 2012.
- Tense: Thì quá khứ đơn.
1.2. Bước 2: Lập dàn ý
Introduction: Paraphrase đề bài.
Overview:
- Overall, the data reveals a notable gender disparity in student enrollment, with females outnumbering males in most subjects, except for Engineering.
- Additionally, there is significant variation in the total number of students among the subjects, with Social Sciences having the highest enrollment and Agriculture the lowest.
| Body paragraph 1 | Body paragraph 2 |
| – In the Social Sciences field, male students numbered fewer than 3,000, while female students amounted to around 4,000, culminating in a total student body of just under 7,000. This was the highest total across all subjects. – Conversely, Engineering saw a predominance of male students, with numbers exceeding 2,000, compared to fewer than 1,000 female students. This resulted in a total enrollment of approximately 3,000. | – For Health, the male student count was over 500, while female students exceeded 1,500, resulting in a total student count surpassing 2,000. – The Humanities department had about 1,000 male students and approximately 1,500 female students, leading to a total of less than 2,500. – In Science and Maths, there were over 1,000 male students and more than 500 female students, with a total number of students falling below 2,000. – Finally, Agriculture had an equal distribution of 100 male and 100 female students, resulting in the smallest total of 200 students. |
Xem thêm:
- Cách viết Topic sentence cho phần thi IELTS Writing
- Cách đọc Bảng nhiều dữ liệu trong IELTS Writing task 1
- Cách nói tăng/ giảm trong IELTS Writing task 1 hay nhất
1.3. Bước 3: Bài mẫu
1.3.1. Bài mẫu band 5.0+
The mixed chart illustrates the number of males and females studying different subjects in 2012, shown in the bar chart, and the total number of students in each subject, presented in the line chart.
Overall, females outnumbered males in most subjects, except in Engineering, where there were more male students. The total number of students in each subject varied, with Social Sciences having the highest total and Agriculture the lowest.
In Social Sciences, there were fewer than 3,000 males and around 4,000 females, with the total number of students being less than 7,000. For Engineering, over 2,000 males and fewer than 1,000 females studied this subject, making the total about 3,000. In Health, over 500 males and more than 1,500 females were enrolled, resulting in a total of over 2,000 students.
The Humanities had about 1,000 male students and approximately 1,500 females, with the total being less than 2,500. Science and Maths had over 1,000 males and more than 500 females, with a total of under 2,000 students. Finally, Agriculture had 100 males and 100 females, with a total of 200 students.
1.3.2. Bài mẫu band 7.0+
The mixed chart illustrates the distribution of male and female students across various subjects in 2012, depicted through a bar chart, and the total number of students in each subject, shown by a line chart.
Overall, the data reveals a notable gender disparity in student enrollment, with females outnumbering males in most subjects, except for Engineering. Additionally, there is significant variation in the total number of students among the subjects, with Social Sciences having the highest enrollment and Agriculture the lowest.
In the Social Sciences field, male students numbered fewer than 3,000, while female students amounted to around 4,000, culminating in a total student body of just under 7,000. This was the highest total across all subjects. Conversely, Engineering saw a predominance of male students, with numbers exceeding 2,000, compared to fewer than 1,000 female students. This resulted in a total enrollment of approximately 3,000.
For Health, the male student count was over 500, while female students exceeded 1,500, resulting in a total student count surpassing 2,000. The Humanities department had about 1,000 male students and approximately 1,500 female students, leading to a total of less than 2,500. In Science and Maths, there were over 1,000 male students and more than 500 female students, with a total number of students falling below 2,000. Finally, Agriculture had an equal distribution of 100 male and 100 female students, resulting in the smallest total of 200 students.
Xem thêm:
- [ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 03/08/2024
- [ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 11/07/2024
- [ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 06/07/2024
- Tổng hợp đề thi IELTS Writing 2024 kèm bài mẫu chi tiết
1.4. Từ vựng
| Từ vựng | Nghĩa |
| Except for /ɪkˈsɛpt fɔːr/ | (phrasal preposition). ngoại trừ E.g.: The conference will take place in the main hall, except for the final session, which will be held in the smaller room. (Hội nghị sẽ diễn ra tại hội trường chính, ngoại trừ phiên họp cuối cùng, sẽ được tổ chức tại phòng nhỏ hơn.) |
| Culminate /ˈkʌlmɪneɪt/ | (verb). đạt đến đỉnh điểm E.g.: The project will culminate in a presentation to the board of directors. (Dự án sẽ đạt đến đỉnh điểm bằng một buổi trình bày trước hội đồng quản trị.) |
| Approximately /əˈprɒksɪmətli/ | (adverb). khoảng chừng, xấp xỉ E.g.: The distance between the two cities is approximately 200 kilometers. (Khoảng cách giữa hai thành phố là khoảng chừng 200 km.) |
| Exceed /ɪkˈsiːd/ | (verb). vượt quá E.g.: The company’s annual revenue exceeded expectations this year. (Doanh thu hàng năm của công ty đã vượt quá mong đợi trong năm nay.) |
| Surpass /sɜːrˈpæs/ | (verb). vượt qua E.g.: Her performance surpassed all expectations. (Màn trình diễn của cô ấy đã vượt qua tất cả các kỳ vọng.) |
1.5. Cấu trúc
1.5.1. Câu phức với While
| S + V + O, while + S + V + O. |
E.g.: Poland had the highest youth unemployment rate, while Denmark had the lowest rates for both youth and overall unemployment.
(Ba Lan có tỷ lệ thất nghiệp trong thanh niên cao nhất, trong khi Đan Mạch có tỷ lệ thất nghiệp thấp nhất cả trong thanh niên lẫn tổng thể.)
1.5.2. Mệnh đề quan hệ có Which
| S + V + O + which + V + O. |
E.g.: I love your cat, which is wearing a hat.
(Tôi thích con mèo của bạn, cái con mà đang đội nón.)
1.5.3. Mệnh đề quan hệ rút gọn
| S + V +O, V_ing + O hoặc S + V + O, V_ed/ V_pp + O. |
E.g.: There was a significant increase in the percentage of families owning one car, reaching the same peak as no-car families in 1971, followed by a slight decline.
(Có một sự gia tăng đáng kể trong tỷ lệ các gia đình sở hữu một xe, đạt đỉnh tương tự như các gia đình không có xe vào năm 1971, theo sau là một sự giảm nhẹ.)
1.6. Lời khuyên từ các Thầy, Cô ở Vietop đối với dạng biểu đồ hỗn hợp (mixed chart) trong IELTS Writing Task 1
1. Hiểu yêu cầu đề bài
- Đọc kỹ đề bài: Đảm bảo bạn hiểu chính xác loại biểu đồ và các yếu tố cần phân tích. Đề bài thường yêu cầu bạn mô tả các xu hướng, so sánh và làm nổi bật các điểm chính.
2. Tổ chức bài viết
- Mở bài (Introduction): Tóm tắt thông tin chính của biểu đồ. Đề cập đến loại biểu đồ, các đơn vị đo lường, và thời gian nếu có.
- Tổng quan (Overview): Mô tả các xu hướng chung và các điểm nổi bật.
- Thân bài (Body paragraphs): Phân tích và so sánh các dữ liệu. Chia thành ít nhất hai đoạn thân bài.
3. Mô tả dữ liệu chính xác
- Sử dụng từ vựng chính xác: Sử dụng các động từ và tính từ mô tả sự thay đổi như “increase,” “decrease,” “remain stable,” “fluctuate,” và các cụm từ chỉ mức độ như “significantly,” “slightly,” “dramatically.”
- So sánh và đối chiếu: Dùng các cấu trúc so sánh như “compared to,” “in contrast to,” và “whereas.”
4. Trình bày dữ liệu
- Sử dụng biểu đồ rõ ràng: Mô tả số liệu một cách rõ ràng và dễ hiểu. Đừng bỏ sót thông tin quan trọng hoặc không liên quan đến yêu cầu của đề bài.
- Tránh liệt kê số liệu: Không liệt kê từng con số một cách nhàm chán. Thay vào đó, tóm tắt và nhóm các số liệu theo các điểm chính.
5. Ngữ pháp và từ vựng
- Đảm bảo ngữ pháp chính xác: Sử dụng các thì đúng và các cấu trúc ngữ pháp phù hợp. Tránh lỗi ngữ pháp như lỗi số nhiều/ ít, và dùng thì quá khứ khi mô tả dữ liệu đã qua.
- Từ vựng đa dạng: Sử dụng từ vựng đa dạng và chính xác để mô tả các xu hướng và số liệu. Tránh lặp từ và sử dụng các từ đồng nghĩa.
6. Đọc và sửa lỗi
- Kiểm tra lỗi: Đọc lại bài viết để phát hiện và sửa các lỗi chính tả, ngữ pháp và dấu câu. Đảm bảo câu văn trôi chảy và dễ hiểu.
- Nhận phản hồi: Nếu có thể, nhờ thầy, cô giáo hoặc những người có chuyên môn cao đọc và cung cấp phản hồi về cách mô tả và phân tích dữ liệu của bạn.
7. Phân tích bài viết mẫu
- Xem xét bài mẫu: Nghiên cứu các bài viết mẫu để hiểu cách tổ chức và trình bày. Phân tích các điểm mạnh và điểm yếu của các bài mẫu để cải thiện bài viết của bạn.
Xem thêm:
- Hướng dẫn cách viết dạng Maps IELTS Writing Task 1
- Cách viết dạng Diagram (Process) IELTS Writing Task 1
- Hướng dẫn cách viết Pie Chart IELTS Writing Task 1
2. IELTS Writing Task 2
| Employers should give their staff at least four weeks’ holiday per year to improve their job performance. To what extent do you agree or disagree? |
| (Các nhà tuyển dụng nên cho nhân viên của họ ít nhất bốn tuần nghỉ phép mỗi năm để cải thiện hiệu suất công việc. Bạn đồng ý hay không đồng ý ở mức độ nào?) |
2.1. Bước 1: Phân tích đề
- Dạng bài: Agree or Disagree (Đưa ra quan điểm cá nhân về một ý kiến).
- Từ khóa: Employers, staff, four weeks’ holiday per year, improve job performance, agree or disagree.
- Phân tích yêu cầu: Đề bài yêu cầu thí sinh đưa ra quan điểm về việc các nhà tuyển dụng có nên cung cấp ít nhất bốn tuần nghỉ phép mỗi năm cho nhân viên của họ nhằm cải thiện hiệu suất công việc hay không. Bạn cần xác định rõ bạn đồng ý hay không đồng ý, hoặc đồng ý một phần với đề xuất này.
2.2. Bước 2: Lập dàn ý
| Introduction: Viết lại đề bài theo cách khác, sau đó đưa ra quan điểm cá nhân. | |
| Body paragraph 1: – Main idea: First of all, having four weeks of holiday allows workers to relax and recharge. + Supporting idea: When people are stressed and tired from working too much, their performance can decrease. For example, if a worker is always tired, they might make more mistakes or not be as creative as they could be. By having a long holiday, they can rest and come back to work with more energy and focus. | Body paragraph 2: – Main idea: On the other hand, giving too much holiday time might cause some problems. + Supporting idea 1: If employees take a long break, they may lose their work rhythm and it can be hard for them to get back into the work routine. + Supporting idea 2: Also, some businesses may not be able to afford to give their employees so much time off. For small companies, losing workers for four weeks could make it difficult to run the business smoothly. |
| Conclusion: Viết lại mở bài theo cách khác, nhắc lại quan điểm cá nhân. Tóm tắt các main idea đã viết trong các đoạn thân bài. | |
Xem thêm:
- Cách viết mở bài Writing Task 2 cuốn hút
- Những mẫu câu và cụm từ “ăn điểm” trong IELTS Writing Task 2
- Cách viết Conclusion trong IELTS Writing task 2
2.3. Bước 3: Bài mẫu
2.3.1. Bài mẫu band 5.0+
In today’s world, it is important for people to balance work and rest. Some people believe that giving employees at least four weeks’ holiday per year can help them improve their job performance. I agree with this idea to some extent, but there are also some reasons why this may not always be the best solution.
First of all, having four weeks of holiday allows workers to relax and recharge. When people are stressed and tired from working too much, their performance can decrease. For example, if a worker is always tired, they might make more mistakes or not be as creative as they could be. By having a long holiday, they can rest and come back to work with more energy and focus.
On the other hand, giving too much holiday time might cause some problems. If employees take a long break, they may lose their work rhythm and it can be hard for them to get back into the work routine. Also, some businesses may not be able to afford to give their employees so much time off. For small companies, losing workers for four weeks could make it difficult to run the business smoothly.
In conclusion, while having a four-week holiday can help workers feel refreshed and improve their performance, it is not always practical for every business. Employers should think carefully about what works best for their company and their employees. In some cases, shorter holidays or other ways to reduce stress might be better options.
2.3.2. Bài mẫu band 7.0+
The notion that employers should grant their employees a minimum of four weeks of vacation annually to enhance job performance is a topic of considerable debate. While there is merit in allowing sufficient time for rest and rejuvenation, there are also valid concerns regarding the potential drawbacks of extensively long holiday breaks. This essay will explore both perspectives before arriving at a reasoned conclusion.
To begin with, providing employees with a four-week holiday enables them to unwind and restore their mental and physical well-being. Extended periods of leave allow workers to escape the pressures of their daily responsibilities, which is essential for preventing burnout. For instance, numerous studies indicate that employees who enjoy regular and adequate vacations experience improved productivity, enhanced creativity, and a marked decrease in stress levels. When individuals return to work after a well-deserved break, they are often more focused and motivated, contributing positively to their overall job performance. Thus, the correlation between adequate holiday time and increased job efficiency cannot be overlooked.
Conversely, the argument against the implementation of lengthy vacation periods stems from concerns about the possible disruption to business operations and employee productivity. A prolonged absence from work may result in a loss of rhythm and workflow, making it challenging for employees to reintegrate into their roles. Furthermore, not all businesses have the financial capacity to support such policies, especially small enterprises where the absence of an employee could severely impact productivity and profitability. In such contexts, frequent long breaks might lead to organizational inefficiencies and could even jeopardize the viability of certain businesses. Therefore, while the benefits of holidays are apparent, the potential challenges they engender must be carefully considered.
In conclusion, while I acknowledge the advantages of offering employees a minimum of four weeks’ holiday each year for improved job performance, it is imperative to balance these benefits against the potential drawbacks. Employers must assess their unique circumstances and work environments to find an optimal solution that promotes employee well-being without compromising operational efficiency. A strategic approach to holiday allocation, which considers both employee health and organizational needs, would likely yield the most favorable outcomes for all parties involved.
2.4. Từ vựng
| Từ vựng | Nghĩa |
| Rejuvenation /rɪˌdʒuːvəˈneɪʃən/ | (noun). sự trẻ hóa, làm mới E.g.: The spa offers various treatments for rejuvenation. (Spa này cung cấp nhiều liệu pháp khác nhau để làm cho trẻ lại.) |
| Burnout /ˈbɜːrnaʊt/ | (noun). sự kiệt sức (do làm việc quá nhiều) E.g.: Employees are at risk of burnout if they work excessively without breaks. (Nhân viên có nguy cơ bị kiệt sức nếu họ làm việc quá sức mà không có thời gian nghỉ ngơi.) |
| Correlation /ˌkɔːrəˈleɪʃən/ | (noun). mối tương quan E.g.: There is a strong correlation between regular exercise and improved mental health. (Có một mối tương quan mạnh mẽ giữa việc tập thể dục đều đặn và sức khỏe tinh thần được cải thiện.) |
| Implementation /ˌɪmplɪmenˈteɪʃən/ | (verb). sự thực hiện E.g.: The implementation of new policies will begin next month. (Việc thực hiện các chính sách mới sẽ bắt đầu vào tháng tới.) |
| Imperative /ɪmˈpɛrətɪv/ | (adjective). cấp bách, bắt buộc E.g.: It is imperative to address this issue immediately. (Việc giải quyết vấn đề này ngay lập tức là rất cấp bách.) |
| Stem from /stɛm frəm/ | (verb phrase). xuất phát từ E.g.: The problem stems from a lack of communication. (Vấn đề xuất phát từ sự thiếu giao tiếp.) |
| Reintegrate into /ˌriːˈɪntɪɡreɪt ˈɪntuː/ | (verb phrase). tái hòa nhập vào E.g.: Returning soldiers may find it challenging to reintegrate into civilian life. (Các binh lính trở về có thể thấy khó khăn khi tái hòa nhập vào cuộc sống dân sự.) |
| Jeopardize /ˈdʒɛpəˌdaɪz/ | (verb). đặt vào nguy cơ E.g.: Ignoring safety procedures could jeopardize the entire project. (Bỏ qua các quy trình an toàn có thể đặt toàn bộ dự án vào nguy cơ.) |
| Engender /ɪnˈdʒɛndər/ | (verb). gây ra, tạo ra E.g.: The new policy engendered a lot of debate among the employees. (Chính sách mới đã gây ra nhiều cuộc tranh luận cho các nhân viên.) |
| Acknowledge /ɪnˈdʒɛndər/ | (verb). thừa nhận E.g.: The company acknowledged the error and issued an apology. (Công ty đã thừa nhận lỗi và phát hành một lời xin lỗi.) |
| Optimal /ˈɒptɪməl/ | (adjective). tối ưu E.g.: Finding the optimal solution requires careful analysis. (Tìm ra giải pháp tối ưu cần phải phân tích cẩn thận.) |
2.5. Cấu trúc
2.5.1. Cấu trúc câu điều kiện với If
| If S + V + O, S + V + O. |
E.g.: If an individual seeks information about historical events, a simple online search can yield extensive results almost instantaneously.
(Nếu một cá nhân tìm kiếm thông tin về các sự kiện lịch sử, một lần tìm kiếm trực tuyến đơn giản có thể mang lại kết quả phong phú gần như ngay lập tức.)
2.5.2. Mệnh đề quan hệ rút gọn
| S + V + O, V_ing + O hoặc S + V + O, Ved +by + O. |
E.g.: Online games can impact children’s eyes, leading to a reduction in their health.
(Trò chơi trực tuyến có thể ảnh hưởng đến mắt của trẻ em, dẫn đến sức khỏe của chúng suy giảm.)
2.5.3. Mệnh đề quan hệ với Which, Who làm chủ ngữ
| S + V + O, which/ who + V + O. |
E.g.: Books are typically authored by experts in their respective fields and undergo stringent editorial review processes prior to publication, which enhances their credibility.
(Sách thường được viết bởi các chuyên gia trong lĩnh vực tương ứng của họ và trải qua các quy trình biên tập khắt khe trước khi xuất bản, điều này làm tăng độ tin cậy của chúng.)
E.g.: This can lead to confusion among users, who may find it difficult to discern fact from fiction.
(Điều này có thể dẫn đến sự nhầm lẫn cho người dùng, khiến họ khó phân biệt được sự thật với hư cấu.)
2.5.4. Cấu trúc câu phức với While
| S + V + O, while S + V + O. |
E.g.: I am a big fan of playing video games, while my best friends love watching movies.
(Tôi rất thích chơi game, trong khi bạn thân của tôi thích xem phim.)
Xem thêm cách viết các dạng bài khác:
- Cách viết dạng Positive & Negative – IELTS Writing Task 2
- Cách viết Discussion Essay trong IELTS Writing Task 2
- Cách viết Problem and Solution trong IELTS Writing Task 2
2.6. Lời khuyên từ các Thầy, Cô ở Vietop đối với dạng Agree or Disagree trong IELTS Writing Task 2
1. Hiểu yêu cầu của đề bài
- Đảm bảo rằng bạn hiểu rõ câu hỏi và yêu cầu của đề bài trước khi bắt đầu viết. Hãy chú ý phân tích xem bạn có đồng ý hoàn toàn, một phần, hay không đồng ý với quan điểm được nêu.
- Việc hiểu rõ đề bài giúp bạn xác định chính xác lập luận cần đưa ra và đảm bảo rằng bạn không đi lạc đề trong bài viết.
2. Xây dựng quan điểm rõ ràng
- Đưa ra quan điểm rõ ràng ngay từ đoạn mở bài và duy trì quan điểm đó xuyên suốt bài viết.
- Một quan điểm rõ ràng giúp bạn dễ dàng xây dựng lập luận và tránh nhầm lẫn cho người đọc.
3. Phát triển lập luận thuyết phục
- Cung cấp các luận điểm mạnh mẽ và dẫn chứng cụ thể để hỗ trợ quan điểm của bạn. Mỗi đoạn thân bài nên tập trung vào một luận điểm chính và được phát triển bằng các ví dụ, số liệu hoặc lý lẽ thuyết phục.
- Những lập luận và dẫn chứng rõ ràng giúp bài viết của bạn có sức thuyết phục hơn và chứng minh được quan điểm của bạn là hợp lý.
4. Đối chiếu quan điểm đối lập
- Đề cập đến quan điểm đối lập trong một đoạn riêng, sau đó giải thích tại sao bạn không đồng ý với quan điểm đó. Điều này giúp bài viết của bạn trở nên cân bằng và thể hiện sự hiểu biết sâu rộng về vấn đề.
- Việc trình bày và phản bác quan điểm đối lập không chỉ giúp bạn thể hiện sự khách quan mà còn làm nổi bật lý do tại sao quan điểm của bạn có sức thuyết phục hơn.
5. Sử dụng ngôn ngữ chính xác
- Sử dụng ngôn ngữ chính xác và các cấu trúc câu đa dạng để làm rõ quan điểm của bạn. Tránh sử dụng các từ ngữ mơ hồ hoặc không chính xác.
- Ngôn ngữ chính xác giúp bài viết của bạn rõ ràng và dễ hiểu hơn, đồng thời nâng cao điểm số về khả năng sử dụng ngôn ngữ trong bài thi.
6. Kết luận tóm tắt và nhấn mạnh
- Tóm tắt các lập luận chính và nhấn mạnh lại quan điểm của bạn trong đoạn kết luận. Đừng giới thiệu thông tin mới ở đoạn này.
- Một kết luận rõ ràng giúp người đọc nhớ lại quan điểm và các lập luận chính của bạn, đồng thời để lại ấn tượng mạnh mẽ.
7. Thực hành và nhận xét phản hồi
- Thực hành viết nhiều bài tập dạng Agree or Disagree và yêu cầu nhận xét từ giáo viên hoặc các nguồn uy tín. Sử dụng phản hồi để cải thiện kỹ năng viết của bạn.
- Việc thực hành thường xuyên và nhận xét phản hồi giúp bạn nhận diện các lỗi thường gặp và nâng cao kỹ năng viết của mình.
Chúng ta đã kết thúc việc phân tích và giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 08/08/2024 với Task 1 thuộc dạng biểu đồ hỗn hợp và Task 2 là dạng Agree or Disagree. Qua quá trình học cách phân tích đề bài, xây dựng dàn ý, và viết bài mẫu, hy vọng các bạn đã trang bị cho mình những kỹ năng cần thiết và cảm thấy tự tin hơn khi đối mặt với các đề thi tương tự trong tương lai. Đừng ngần ngại để lại câu hỏi trong phần bình luận nếu cần sự hỗ trợ kịp thời từ thầy.
Để chuẩn bị tốt hơn cho kỳ thi IELTS sắp tới, bạn có thể tham khảo các tài liệu và đề thi mẫu do Vietop English biên soạn. Những tài liệu này không chỉ giúp bạn làm quen với cấu trúc đề thi mà còn cung cấp các bài viết mẫu chi tiết, hỗ trợ bạn nâng cao kỹ năng viết một cách hiệu quả.
Để đạt được kết quả như mong muốn trong phần thi IELTS Writing, việc luyện tập đều đặn và nhận phản hồi từ giáo viên là vô cùng cần thiết. Nếu bạn cần sự hỗ trợ tận tâm từ đội ngũ giảng viên, các khóa học IELTS tại Vietop sẽ là lựa chọn hoàn hảo giúp bạn đạt được mục tiêu IELTS của mình. Hãy bắt đầu học IELTS cùng Vietop ngay hôm nay để biến nỗ lực của bạn thành kết quả xứng đáng!
Chúc các bạn ôn tập tốt và đạt được kết quả cao trong kỳ thi IELTS sắp tới!

![[ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 27/01/2026](https://vietop.edu.vn/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/thumbnail-giai-de-ielts-writing-ngay-27-01-2026.jpg)

![[ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 07/04/2025](https://vietop.edu.vn/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/giai-de-ielts-writing-ngay-07-04-2025.png)

![[ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 15/03/2025](https://vietop.edu.vn/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/giai-de-ielts-writing-ngay-15-03-2025.jpg)
![[ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 22/03/2025](https://vietop.edu.vn/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/giai-de-ielts-writing-ngay-22-03-2025.jpg)
![[ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 08/03/2025](https://vietop.edu.vn/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/giai-de-ielts-writing-ngay-08-03-2025.jpg)
![[ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 06/03/2025](https://vietop.edu.vn/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/giai-de-ielts-writing-ngay-06-03-2025.jpg)
