Trong phần thi IELTS Writing task 1, dạng bài mô tả bảng số liệu (table) là một trong những dạng bài phổ biến. Việc hiểu rõ cách phân tích và trình bày bảng số liệu không chỉ giúp bạn đạt điểm cao mà còn nâng cao kỹ năng viết học thuật. Dạng bài này đã xuất hiện trong đề thi ngày 20/07/2024 vừa qua.
Hãy cùng xem xét đề thi của task 1 và task 2 để hiểu cách làm bài:
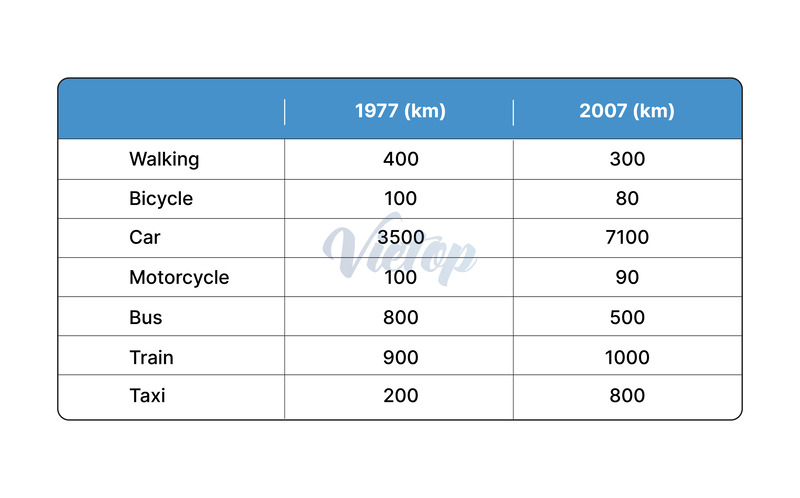
- Đề IELTS Writing task 1: The table below gives information about the average annual distance travelled by adults and the types of travel in 1977 and 2007. Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features and make comparisons where relevant.
- Đề IELTS Writing task 2 thuộc dạng Advantages and Disadvantages với chủ đề Lifestyle: In the past, people stored knowledge in books. Nowadays, people store knowledge on the internet. Do you think the advantages outweigh the disadvantages?
Để nắm vững cách viết task 1 và task 2 trong IELTS Writing, chúng ta sẽ phân tích bảng số liệu trong task 1, xem xét các ưu và nhược điểm, và sau đó đưa ra quan điểm cá nhân trong task 2 bằng cách tham khảo các bài mẫu theo từng band điểm từ bài giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 20/07/2024.
1. IELTS Writing task 1
| The table below gives information about the average annual distance travelled by adults and the types of travel in 1977 and 2007. Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features and make comparisons where relevant. |
| (Bảng dưới đây cung cấp thông tin về khoảng cách trung bình hàng năm mà người lớn di chuyển và các loại hình di chuyển vào các năm 1977 và 2007. Tóm tắt thông tin bằng cách chọn và báo cáo các đặc điểm chính và so sánh khi cần thiết.) |
1.1. Bước 1: Phân tích đề
- Dạng biểu đồ: Bảng số liệu có sự thay đổi về thời gian.
- Topic: Khoảng cách trung bình hàng năm mà người lớn di chuyển và các loại hình di chuyển.
- Place: Không đề cập.
- Number of factors: 7.
- Time: 1977 và 2007.
- Tense: Thì quá khứ đơn.
1.2. Bước 2: Lập dàn ý
Introduction: Paraphrase đề bài.
- There was a significant disparity in the distances covered by different transport modes over the two decades, with notable increases in the utilization of cars, trains, and taxis, while other forms of travel experienced a decline.
| Body paragraph 1 | Body paragraph 2 |
| – Both activities witnessed a reduction in average distance traveled. Specifically, walking decreased from 400 kilometers in 1977 to 300 kilometers in 2007, marking a decline of 100 kilometers. – Bicycle travel saw a drop from 100 kilometers to 80 kilometers during the same period, reflecting a decrease of 20 kilometers. – Motorcycling exhibited a marginal decrease, with average distances traveled falling from 100 kilometers to 90 kilometers. | – Car travel surged dramatically, with adults covering an average of 3,500 kilometers in 1977, which more than doubled to 7,100 kilometers by 2007, indicating an increase of 3,600 kilometers. – Taxi usage also showed remarkable growth, rising from 200 kilometers in 1977 to 800 kilometers in 2007, a notable increment of 600 kilometers. – The use of buses saw a decline from 800 kilometers to 500 kilometers, while train travel experienced a slight increase, from 900 kilometers to 1,000 kilometers, signifying a change of 100 kilometers. |
Xem thêm:
- Hướng dẫn cách viết introduction task 1 đơn giản cực hấp dẫn
- Cách đọc Bảng nhiều dữ liệu trong IELTS Writing task 1
- Cách nói tăng/ giảm trong IELTS Writing task 1 hay nhất
1.3. Bước 3: Bài mẫu
1.3.1. Bài mẫu band 5.0+
The table compares the average distances adults traveled by different modes of transport in 1977 and 2007.
Overall, while travelling by car, train, and taxi witnessed an increase, walking, cycling, motorcycling, and travelling by bus saw a decline.
Specifically, walking dropped from 400 kilometers in 1977 to 300 kilometers in 2007, a decrease of 100 kilometers. Cycling also fell from 100 kilometers to 80 kilometers, a reduction of 20 kilometers. Motorcycling experienced a slight decrease from 100 kilometers to 90 kilometers.
In contrast, car travel increased significantly. The average distance covered by cars rose from 3,500 kilometers in 1977 to 7,100 kilometers in 2007. Taxi usage also grew substantially, from 200 kilometers to 800 kilometers. Bus travel decreased from 800 kilometers to 500 kilometers, while train travel slightly increased from 900 kilometers to 1,000 kilometers.
1.3.2. Bài mẫu band 7.0+
The table presents a comparative analysis of the average annual distances traversed by adults across various modes of transportation in the years 1977 and 2007.
Overall, there was a significant disparity in the distances covered by different transport modes over the two decades, with notable increases in the utilization of cars, trains, and taxis, while other forms of travel experienced a decline.
In terms of walking and cycling, both activities witnessed a reduction in average distance traveled. Specifically, walking decreased from 400 kilometers in 1977 to 300 kilometers in 2007, marking a decline of 100 kilometers. Similarly, bicycle travel saw a drop from 100 kilometers to 80 kilometers during the same period, reflecting a decrease of 20 kilometers. Conversely, motorcycling exhibited a marginal decrease, with average distances traveled falling from 100 kilometers to 90 kilometers.
In stark contrast, car travel surged dramatically, with adults covering an average of 3,500 kilometers in 1977, which more than doubled to 7,100 kilometers by 2007, indicating an increase of 3,600 kilometers. Taxi usage also showed remarkable growth, rising from 200 kilometers in 1977 to 800 kilometers in 2007, a notable increment of 600 kilometers. The use of buses saw a decline from 800 kilometers to 500 kilometers, while train travel experienced a slight increase, from 900 kilometers to 1,000 kilometers, signifying a change of 100 kilometers.
Xem ngay: Khoá học IELTS Junior giúp bạn xây dựng nền tảng vững chắc, phát triển tư duy toàn diện
1.4. Từ vựng
| Từ vựng | Nghĩa |
| Significant disparity /sɪɡˈnɪfɪkənt dɪˈspærɪti/ | (noun phrase). sự khác biệt đáng kể E.g.: The report highlights a significant disparity in income levels between different regions. (Báo cáo nêu rõ sự khác biệt đáng kể về mức thu nhập giữa các khu vực khác nhau.) |
| Witness a reduction /ˈwɪtnəs ə rɪˈdʌkʃən/ | (collocation). chứng kiến sự giảm sút E.g.: The company witnessed a reduction in sales last quarter. (Công ty đã chứng kiến sự giảm sút trong doanh số bán hàng của quý trước.) |
| Specifically /spɪˈsɪfɪkli/ | (adverb). cụ thể E.g.: The new policy specifically targets reducing carbon emissions. (Chính sách mới cụ thể nhắm đến việc giảm khí thải carbon.) |
| In stark contrast /ɪn stɑːrk ˈkɒntrɑːst/ | (phrase). ngược lại hoàn toàn E.g.: In stark contrast to the previous year, this year’s profits have soared. (Ngược lại hoàn toàn so với năm trước, lợi nhuận của năm nay đã tăng vọt.) |
| Notable increment /ˈnoʊtəbl ˈɪnkrəmənt/ | (noun phrase). sự gia tăng đáng chú ý E.g.: There was a notable increment in the number of visitors this month. (Có sự gia tăng đáng chú ý trong số lượng khách thăm trong tháng này.) |
| Signify /ˈsɪɡnɪfaɪ/ | (verb). báo hiệu, biểu thị E.g.: The red light signifies that you need to stop. (Đèn đỏ biểu thị rằng bạn cần phải dừng lại.) |
Xem thêm:
- Cách làm dạng bài Bar Chart IELTS Writing Task 1
- Cách viết dạng Diagram (Process) IELTS Writing Task 1
- Cách viết Writing Task 1 Line Graph
1.5. Cấu trúc
1.5.1. Câu phức với While
S + V + O, while + S + V + O.
E.g.: Poland had the highest youth unemployment rate, while Denmark had the lowest rates for both youth and overall unemployment.
(Ba Lan có tỷ lệ thất nghiệp trong thanh niên cao nhất, trong khi Đan Mạch có tỷ lệ thất nghiệp thấp nhất cả trong thanh niên lẫn tổng thể.)
1.5.2. Mệnh đề quan hệ có Which
S + V + O + which + V + O.
E.g.: I love your cat, which is wearing a hat.
(Tôi thích con mèo của bạn, cái con mà đang đội nón.)
1.5.3. Mệnh đề quan hệ rút gọn
S + V +O, V_ing + O hoặc S + V + O, V_ed/ V_pp + O.
E.g.: There was a significant increase in the percentage of families owning one car, reaching the same peak as no-car families in 1971, followed by a slight decline.
(Có một sự gia tăng đáng kể trong tỷ lệ các gia đình sở hữu một xe, đạt đỉnh tương tự như các gia đình không có xe vào năm 1971, theo sau là một sự giảm nhẹ.)
2. IELTS Writing task 2
| In the past, people stored knowledge in books. Nowadays, people store knowledge on the internet. Do you think the advantages outweigh the disadvantages? |
| (Trong quá khứ, con người lưu trữ kiến thức trong sách. Ngày nay, con người lưu trữ kiến thức trên internet. Bạn có nghĩ rằng những lợi ích vượt trội hơn so với những bất lợi không?) |
2.1. Bước 1: Phân tích đề
- Dạng bài: Advantages and disadvantages kèm theo quan điểm cá nhân.
- Từ khóa: In the past, people stored knowledge, books, nowadays, internet, advantages, disadvantages, outweigh.
- Phân tích yêu cầu: Đề bài yêu cầu thí sinh phân tích các lợi ích và hạn chế của việc chuyển đổi lưu trữ kiến thức từ sách sang internet, và đưa ra đánh giá cá nhân về xu hướng này.
2.2. Bước 2: Lập dàn ý
| Introduction: Viết lại đề bài theo cách khác, sau đó đưa ra quan điểm cá nhân. | |
| Body paragraph 1: | Body paragraph 2: |
| – Main idea: Advantages of this change. + Supporting idea: The internet is very easy to use for finding information. People can search for what they need quickly. For instance, if someone wants to learn about a historical event, they can find detailed information online within a few seconds. This is much faster compared to looking through many books. + Supporting idea: The internet has a huge amount of information available, so people do not need to buy and store a lot of books. This can save money and space. | – Main idea: Disadvantages of this change. + Supporting idea: The internet has a lot of wrong information. Anyone can write online, and it can be wrong. This can make people confused and not know what to believe. In contrast, books are usually written by experts and checked before publishing, so they are more reliable. + Supporting idea: The internet can be very distracting. When people look for information online, they might start using social media, playing games, or visiting other websites. This wastes time and makes it hard to study or work. With books, people can focus better because there are no distractions. + Supporting idea: The internet needs electricity and a device to use it. Not everyone has these. Books do not need electricity and can be used anywhere. This makes books easier for everyone to use. |
| Conclusion: Viết lại mở bài theo cách khác, nhắc lại quan điểm cá nhân. Tóm tắt các main idea đã viết trong các đoạn thân bài. | |
Xem thêm:
- Cách viết mở bài Writing Task 2 cuốn hút
- Cách viết Topic sentence cho phần thi IELTS Writing
- Cách viết Conclusion trong IELTS Writing task 2
2.3. Bước 3: Bài mẫu
2.3.1. Bài mẫu band 5.0+
In the past, people kept knowledge in books. Nowadays, people use the internet to store knowledge. I think the disadvantages of this are more significant than the advantages.
On the one hand, the internet is very easy to use for finding information. People can search for what they need quickly. For instance, if someone wants to learn about a historical event, they can find detailed information online within a few seconds. This is much faster compared to looking through many books. Additionally, the internet has a huge amount of information available, so people do not need to buy and store a lot of books. This can save money and space.
However, there are many problems. One problem is that the internet has a lot of wrong information. Anyone can write online, and it can be wrong. This can make people confused and not know what to believe. In contrast, books are usually written by experts and checked before publishing, so they are more reliable. Another problem is that the internet can be very distracting. When people look for information online, they might start using social media, playing games, or visiting other websites. This wastes time and makes it hard to study or work. With books, people can focus better because there are no distractions. Moreover, the internet needs electricity and a device to use it. Not everyone has these. Books do not need electricity and can be used anywhere. This makes books easier for everyone to use.
In conclusion, while the internet is easy for finding information, the problems with wrong information, distractions, and needing electricity make it less good than books. So, I think the disadvantages of the internet outweigh the advantages.
Cách trình bày ý tưởng ở dạng bài advantage and disadvantage với chủ đề lifestyle – chủ đề khá quen thuộc và gần gũi trong đời sống để đạt điểm cao trong bài thi? Khoá học IELTS 3.0 – 5.0 – IELTS cơ bản giúp bạn có tư duy học IELTS đúng cách và phương pháp làm bài hiệu quả. Tham khảo ngay!
2.3.2. Bài mẫu band 7.0+
Historically, knowledge was predominantly recorded in books. In contemporary society, however, the internet has emerged as the primary repository for information. In my opinion, the drawbacks associated with online knowledge storage significantly outweigh its benefits.
On the one hand, the internet offers unparalleled convenience for information retrieval. Users can effortlessly search for specific queries and obtain results within seconds. For instance, if an individual seeks information about historical events, a simple online search can yield extensive results almost instantaneously, a stark contrast to the time-consuming process of sifting through multiple books. Moreover, the vast repository of the internet negates the necessity for purchasing numerous texts, thus reducing financial burdens on users.
On the other hand, the internet is fraught with challenges that can undermine its reliability. One major concern is the prevalence of misinformation. The open-access nature of the internet allows virtually anyone to publish content, often without rigorous verification. This can lead to confusion among users, who may find it difficult to discern fact from fiction. In contrast, books are typically authored by experts in their respective fields and undergo stringent editorial review processes prior to publication, which enhances their credibility. Additionally, the internet can be a significant source of distraction. While searching for information, individuals may easily divert their attention to social media platforms, online games, or unrelated websites. This phenomenon not only consumes valuable time but also hampers one’s ability to concentrate on academic or professional tasks. On the contrary, the tactile experience of engaging with physical books fosters a more focused and undisturbed learning environment. Furthermore, the internet’s dependency on electricity and electronic devices presents an accessibility issue. Not everyone has consistent access to these technological resources, while printed books are universally available and can be utilized in any setting without reliance on power sources.
In conclusion, although the internet facilitates quick access to information, the challenges posed by misinformation, distractions, and technological dependence suggest that it is a less effective medium for knowledge storage compared to traditional books. Therefore, I firmly believe that the disadvantages of using the internet for knowledge preservation outweigh any advantages it may present.
2.4. Từ vựng
| Từ vựng | Nghĩa |
| Emerge (as) /ɪˈmɜːrdʒ/ | (verb). xuất hiện, nổi lên (như là) E.g.: New trends emerge every year in the fashion industry. (Các xu hướng mới xuất hiện mỗi năm trong ngành công nghiệp thời trang.) |
| Unparalleled convenience /ʌnˈpærəˌlɛld kənˈviːniəns/ | (noun phrase). sự tiện lợi vô song E.g.: The new app offers unparalleled convenience for managing your finances. (Ứng dụng mới mang lại sự tiện lợi vô song trong việc quản lý tài chính của bạn.) |
| Effortlessly /ˈɛfərtləsli/ | (adverb). một cách dễ dàng E.g.: She completed the task effortlessly due to her experience. (Cô ấy hoàn thành nhiệm vụ một cách dễ dàng nhờ vào kinh nghiệm của mình.) |
| Instantaneously /ˌɪnstənˈteɪniəsli/ | (adverb). ngay lập tức E.g.: Information can be transmitted instantaneously over the internet. (Thông tin có thể được truyền ngay lập tức qua internet.) |
| Prevalence /ˈprɛvələns/ | (noun). tính phổ biến E.g.: The prevalence of smartphones has changed the way we communicate. (Tính phổ biến của điện thoại thông minh đã thay đổi cách chúng ta giao tiếp.) |
| Rigorous verification /ˈrɪɡərəs ˌvɛrɪfɪˈkeɪʃən/ | (noun phrase). kiểm tra nghiêm ngặt E.g.: The study was conducted with rigorous verification to ensure accuracy. (Nghiên cứu được thực hiện với sự kiểm tra nghiêm ngặt để đảm bảo độ chính xác.) |
| Stringent /ˈstrɪndʒənt/ | (adjective). khắt khe E.g.: The company has stringent safety protocols to prevent accidents. (Công ty có các quy trình an toàn khắt khe để ngăn ngừa tai nạn.) |
| Hamper /ˈhæmpər/ | (verb). cản trở E.g.: The bad weather may hamper our travel plans. (Thời tiết xấu có thể cản trở kế hoạch đi lại của chúng tôi.) |
Xem thêm cách viết các dạng bài khác:
- Cách viết dạng Positive & Negative – IELTS Writing Task 2
- Cách viết Discussion Essay trong IELTS Writing Task 2
- Cách viết Problem and Solution trong IELTS Writing Task 2
2.5. Cấu trúc
2.5.1. Cấu trúc câu điều kiện với If
If S + V + O, S + V + O.
E.g.: If an individual seeks information about historical events, a simple online search can yield extensive results almost instantaneously.
(Nếu một cá nhân tìm kiếm thông tin về các sự kiện lịch sử, một lần tìm kiếm trực tuyến đơn giản có thể mang lại kết quả phong phú gần như ngay lập tức.)
2.5.2. Mệnh đề quan hệ rút gọn
S + V + O, V_ing + O hoặc S + V + O, Ved +by + O.
E.g.: Online games can impact children’s eyes, leading to a reduction in their health.
(Trò chơi trực tuyến có thể ảnh hưởng đến mắt của trẻ em, dẫn đến sức khỏe của chúng suy giảm.)
2.5.3. Mệnh đề quan hệ với Which, Who làm chủ ngữ
S + V + O, which/ who + V + O.
E.g.: Books are typically authored by experts in their respective fields and undergo stringent editorial review processes prior to publication, which enhances their credibility.
(Sách thường được viết bởi các chuyên gia trong lĩnh vực tương ứng của họ và trải qua các quy trình biên tập khắt khe trước khi xuất bản, điều này làm tăng độ tin cậy của chúng.)
E.g.: This can lead to confusion among users, who may find it difficult to discern fact from fiction.
(Điều này có thể dẫn đến sự nhầm lẫn cho người dùng, khiến họ khó phân biệt được sự thật với hư cấu.)
2.5.4. Cấu trúc câu phức với While
S + V + O, while S + V + O.
E.g.: I am a big fan of playing video games, while my best friends love watching movies.
(Tôi rất thích chơi game, trong khi bạn thân của tôi thích xem phim.)
Xem thêm:
- [ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 11/07/2024
- [ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 06/07/2024
- [ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 22/06/2024
- [ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 15/06/2024
Chúng ta vừa hoàn thành việc phân tích và giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 20/07/2024, bao gồm cả task 1 với dạng bảng số liệu và task 2 với dạng bài phân tích ưu, nhược điểm và nêu quan điểm cá nhân. Sau khi học cách phân tích đề, lập dàn ý và viết bài mẫu, các bạn cảm thấy thế nào về đề thi hôm nay? Nếu có bất kỳ câu hỏi nào, hãy để lại bình luận dưới bài viết để thầy có thể trả lời kịp thời.
Để nắm bắt xu hướng đề thi IELTS Writing trong tương lai, các bạn có thể tham khảo bộ đề tổng hợp IELTS Writing năm 2024 do thầy và đội ngũ biên tập của Vietop English biên soạn. Bộ đề này không chỉ bao gồm các đề thi mà còn có các bài mẫu chi tiết, giúp các bạn ôn luyện hiệu quả.
Để đạt được điểm số mong muốn trong IELTS Writing, việc luyện tập đều đặn và nhận phản hồi từ các giáo viên là rất quan trọng. Nếu bạn đang tìm kiếm sự hỗ trợ tận tình từ giáo viên, các khóa học IELTS tại Vietop chính là lựa chọn lý tưởng để bạn hoàn thành mục tiêu IELTS của mình. Đừng để thời gian và công sức của bạn bị lãng phí – hãy bắt đầu học IELTS cùng Vietop ngay hôm nay!
Chúc các bạn thành công trong kỳ thi IELTS sắp tới!

![[ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 27/01/2026](https://vietop.edu.vn/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/thumbnail-giai-de-ielts-writing-ngay-27-01-2026.jpg)

![[ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 07/04/2025](https://vietop.edu.vn/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/giai-de-ielts-writing-ngay-07-04-2025.png)

![[ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 15/03/2025](https://vietop.edu.vn/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/giai-de-ielts-writing-ngay-15-03-2025.jpg)
![[ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 22/03/2025](https://vietop.edu.vn/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/giai-de-ielts-writing-ngay-22-03-2025.jpg)
![[ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 08/03/2025](https://vietop.edu.vn/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/giai-de-ielts-writing-ngay-08-03-2025.jpg)
![[ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 06/03/2025](https://vietop.edu.vn/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/giai-de-ielts-writing-ngay-06-03-2025.jpg)
