Trong kỳ thi IELTS Writing diễn ra vào ngày 28/12/2024, các thí sinh đã gặp phải hai dạng bài: Bar Chart trong Writing Task 1 và bài luận dạng Negative or Positive Development trong Writing Task 2.
Trong bài viết này, mình sẽ hướng dẫn bạn cách phân tích đề, xây dựng dàn ý chi tiết, và chia sẻ những mẹo hữu ích để bạn có thể làm bài một cách tự tin và hiệu quả.
Trước tiên, mình sẽ cho bạn xem đề thi cụ thể:
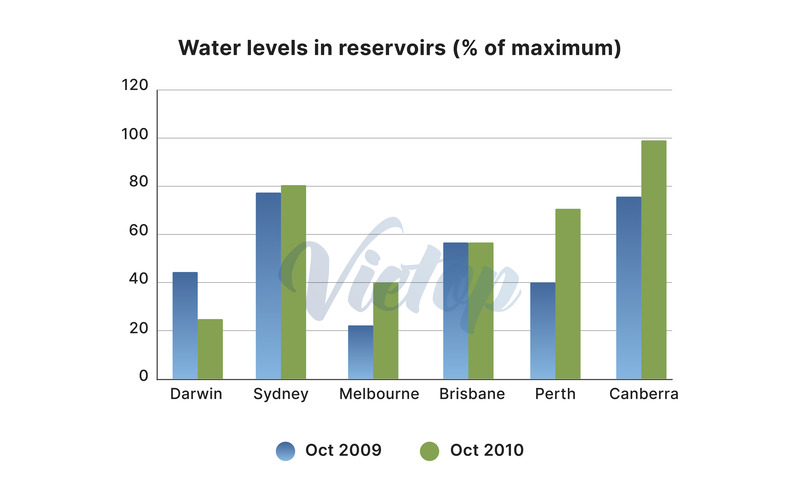
- Đề IELTS Writing Task 1: The charts below show the water levels of 6 cities in Australia in October 2009 and 2010. Summarize the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
- Đề IELTS Writing Task 2: Nowadays more tasks at home and work are being performed by robots. Is this a negative or positive development?
Ngoài ra, mình sẽ cung cấp các bài mẫu band 5.0+ và 7.5+ để bạn có thể dễ dàng so sánh, qua đó nhận biết sự khác biệt trong việc sử dụng từ vựng và cấu trúc câu trong bài giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 28/12/2024 sau.
Và bây giờ, cùng mình học bài thôi!
1. IELTS Writing Task 1
| The charts below show the water levels of 6 cities in Australia in October 2009 and 2010. Summarize the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant. |
| (Biểu đồ dưới đây thể hiện mực nước của 6 thành phố ở Úc vào tháng 10/2009 và tháng 10/2010. Tóm tắt thông tin bằng cách lựa chọn và báo cáo những điểm chính, và so sánh dữ liệu liên quan.) |
1.1. Bước 1: Phân tích đề
- Dạng biểu đồ: Bar Chart
- Topic: Mực nước ở các thành phố ở Úc trong 2 thời điểm
- Number of factors: 6
- Time: tháng 10 năm 2009 và 2010
- Tense: Các thì quá khứ
- Nhóm dữ liệu: Chia theo 2 nhóm:
- Nhóm 1: Mực nước của 6 thành phố ở thời điểm tháng 10/2009.
- Nhóm 2: Mực nước của 6 thành phố ở thời điểm tháng 10/2010.
- => Có 2 đoạn thân bài.
1.2. Bước 2: Lập dàn ý
Introduction: Paraphrase đề bài.
Overview:
- Most cities experienced improvements in water levels.
- Perth showed the most substantial growth.
- Canberra reached full capacity.
- Darwin saw a significant decline, while Brisbane’s levels remained unchanged.
| Body paragraph 1 (10/2009) | Body paragraph 2 (10/2010) |
| – Highest levels: Sydney (~80%) and Canberra (~70%). – Moderate levels: Brisbane (~60%), Darwin (~40%), and Perth (~40%). – Lowest level: Melbourne (~20%). | – Significant increases: + Canberra reached 100% + Sydney rose to 80% + Perth climbed from 40% to nearly 80% + Melbourne doubled to 40% – No change: Brisbane remained at 60% – Significant decline: Darwin dropped from over 40% to around 20%. |
1.3. Bước 3: Bài mẫu
1.3.1. Bài mẫu band 5.0+
The bar chart shows the percentage of water levels in reservoirs for six cities in Australia in October 2009 and October 2010.
Overall, most cities had more water in 2010 than in 2009. Perth had the biggest increase, while Darwin’s water levels went down a lot. Brisbane stayed the same.
In October 2009, Sydney had the highest water level at around 80%, and Canberra was next with about 70%. Brisbane’s water levels were close to 60%. Darwin and Perth were both above 40%, but Darwin was a little higher. Melbourne had the lowest water levels, just above 20%.
In October 2010, Canberra’s water levels reached 100%, and Sydney went up a little to 80%. Perth’s water levels went up the most, rising from above 40% to about 80%. Melbourne’s water levels also went up, doubling to about 40%. Brisbane stayed the same at 60%. Darwin had the biggest drop, falling from above 40% to about 20%.
1.3.2. Bài mẫu band 7.5+
The bar chart illustrates the percentage of maximum water levels in reservoirs across six Australian cities – Darwin, Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth, and Canberra – for October 2009 and October 2010.
Overall, water levels improved across most cities between the two periods, with Perth experiencing the most substantial growth and Canberra achieving full capacity by 2010. However, Darwin saw a significant decline, and Brisbane’s levels remained unchanged.
In October 2009, water levels in reservoirs displayed noticeable variations across the six cities. Sydney had the highest levels, nearing 80% of maximum capacity, while Canberra followed closely at around 70%. Brisbane recorded water levels at nearly 60%, making it the third-highest city. Darwin and Perth showed similar levels, both slightly above 40%, although Darwin was marginally higher. In contrast, Melbourne had the lowest water levels, slightly above 20%, indicating a severe shortage in comparison to the other cities.
By October 2010, the water levels in reservoirs showed significant changes in most cities. Canberra’s reservoirs reached full capacity at 100%, while Sydney experienced a slight increase, reaching 80%. Brisbane’s water levels remained steady at approximately 60%. Darwin, however, saw a sharp decline, dropping from over 40% to around 20%. Perth experienced the most dramatic rise, climbing from just above 40% to nearly 80%. Melbourne also saw a notable improvement, doubling its previous level to reach about 40%.
1.4. Từ vựng
| Từ vựng | Nghĩa |
| Reservoir /ˈrez.ɚ.vwɑːr/ | (noun) hồ chứa nước E.g.They built a reservoir to store water during the dry season. (Họ xây một hồ chứa nước để trữ nước vào mùa khô.) |
| Substantial /səbˈstæn.ʃəl/ | (adjective) đáng kể, lớn lao E.g. The project requires a substantial investment of time and resources. (Dự án đòi hỏi một sự đầu tư đáng kể về thời gian và nguồn lực.) |
| Full capacity /fʊl kəˈpæs.ə.ti/ | (noun phrase) công suất tối đa, sức chứa đầy đủ E.g. The factory is now operating at full capacity. (Nhà máy hiện đang hoạt động với công suất tối đa.) |
| Noticeable variations /ˈnoʊ.t̬ɪ.sə.bəl ˌver.iˈeɪ.ʃənz/ | (noun phrase) sự khác biệt/ biến thiên rõ rệt E.g. The experiment showed noticeable variations in the results from different groups. (Thí nghiệm cho thấy sự biến thiên rõ rệt trong kết quả giữa các nhóm khác nhau.) |
| Marginally /ˈmɑːr.dʒɪ.nəl.i/ | (adverb) một chút, không đáng kể E.g. The cost of living has increased marginally in recent years. (Chi phí sinh hoạt đã tăng nhẹ trong những năm gần đây.) |
| Severe /səˈvɪr/ | (adjective) nghiêm trọng E.g. The storm caused severe damage to the coastal areas. (Cơn bão đã gây thiệt hại nghiêm trọng cho các khu vực ven biển.) |
| Shortage /ˈʃɔːr.t̬ɪdʒ/ | (noun) sự thiếu hụt, sự khan hiếm E.g.There is a shortage of skilled workers in the construction industry. (Có sự thiếu hụt lao động có tay nghề trong ngành xây dựng.) |
| Approximately /əˈprɑːk.sə.mət.li/ | (adverb) xấp xỉ, khoảng chừng E.g. The journey will take approximately two hours. (Chuyến đi sẽ mất khoảng chừng hai tiếng.) |
| Sharp decline /ʃɑːrp dɪˈklaɪn/ | (noun phrase) sự giảm mạnh E.g. Stock prices experienced a sharp decline after the market opened. (Giá cổ phiếu đã giảm mạnh ngay sau khi thị trường mở cửa.) |
| Dramatic rise /drəˈmæt.ɪk raɪz/ | (noun phrase) sự tăng vọt, gia tăng đáng kể E.g. After the release of their new product, the company experienced a dramatic rise in sales. (Sau khi ra mắt sản phẩm mới, doanh số bán hàng của công ty tăng vọt.) |
| Notable improvement /ˈnoʊ.t̬ə.bəl ɪmˈpruːv.mənt/ | (noun phrase) sự cải thiện đáng chú ý E.g. Her writing skills show notable improvement after attending the workshop. (Kỹ năng viết của cô ấy đã cải thiện đáng chú ý sau khi tham dự buổi hội thảo.) |
1.5. Cấu trúc
1.5.1. Câu phức với cụm trạng ngữ
| S1 + V1 + O1, with + S2 + V_ing2 + O2 + and + S3 + V_ing3 + O3 |
E.g. Water levels improved across most cities between the two periods, with Perth experiencing the most substantial growth and Canberra achieving full capacity by 2010.
(Mực nước đã cải thiện ở hầu hết các thành phố giữa hai giai đoạn, với Perth đạt mức tăng trưởng đáng kể nhất và Canberra đạt công suất tối đa vào năm 2010.)
- Mệnh đề chính: “Water levels improved across most cities between the two periods”
- Cụm trạng ngữ: “with Perth experiencing the most substantial growth and Canberra achieving full capacity by 2010.” Trong đó, có 2 cụm hiện tại phân từ:
- Cụm hiện tại phân từ 1: “Perth experiencing the most substantial growth”
- Cụm hiện tại phân từ 2: “Canberra achieving full capacity by 2010.”
=> Cụm trạng ngữ đóng vai trò bổ sung thông tin cho mệnh đề chính, giúp câu đầy đủ nghĩa và mang được nhiều thông tin hơn.
=> Thể hiện trình độ ngữ pháp nâng cao.
1.5.2. Phép song song
Phép song song trong cụ thể ví dụ sau sử dụng sự song song trong cấu trúc câu:
| S1 + V_ing + O1, S2 + V_ing + O2 |
Xem thêm: Cấu trúc song song
E.g. “….with Perth experiencing the most substantial growth and Canberra achieving full capacity by 2010.”
(…với Perth đạt mức tăng trưởng đáng kể nhất và Canberra đạt công suất tối đa vào năm 2010.)
=> “Perth experiencing the most substantial growth” và “Canberra achieving full capacity by 2010” có sự song song trong cấu trúc, đặc biệt là trong việc sử dụng hiện tại phân từ “experiencing” và “achieving”.
=> Giúp câu văn có nhịp điệu, làm tăng tính dễ đọc.
Xem thêm các bài giải mẫu khác:
- [ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 21/12/2024
- [ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 14/12/2024
- [ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 05/12/2024
- Tổng hợp đề thi IELTS Writing 2024 kèm bài mẫu chi tiết – Cập nhật liên tục
2. IELTS Writing Task 2
| Nowadays more tasks at home and work are being performed by robots. Is this a negative or positive development? |
| (Ngày nay, ngày càng có nhiều công việc ở nhà và nơi làm việc được thực hiện bởi robot. Đây là một sự phát triển tiêu cực hay tích cực?) |
2.1. Bước 1: Phân tích đề
- Dạng bài: Positive/ Negative Development
- Từ khóa: more tasks at home and work, performed by robots, negative or positive development
- Phân tích yêu cầu: Đề đưa ra thực trạng: Ngày nay càng nhiều công việc ở nhà và ở chỗ làm được thực hiện bằng robot, và hỏi bạn đây là một sự phát triển tích cực hay tiêu cực
=> Bài viết theo hướng negative development. Mình sẽ cung cấp 2 lý do chính tại sao mình nghĩ đây là một negative development
- Lý do 1: People may lose essential skills over time and become overly reliant on technology.
(Con người có thể đánh mất những kỹ năng quan trọng theo thời gian và trở nên dựa dẫm quá mức vào công nghệ.)- Ví dụ: Tasks like cooking, cleaning, and decision-making are fundamental, and their neglect could lead to a decline in individual independence and problem-solving capabilities.
(Những đầu việc như nấu ăn, dọn dẹp, quyết định là những đầu việc cơ bản của con người, và việc dựa dẫm vào công nghệ sẽ khiến cho khả năng tự lập và giải quyết vấn đề của con người bị suy giảm)
- Ví dụ: Tasks like cooking, cleaning, and decision-making are fundamental, and their neglect could lead to a decline in individual independence and problem-solving capabilities.
- Lý do 2: Robots and AI systems often rely on data collection to perform tasks, which raises concerns about data security and breaches of personal privacy.
(Robot và các hệ thống AI thường dựa vào việc thu thập dữ liệu để hoạt động, làm dấy lên những quan ngại về an ninh dữ liệu và xâm phạm sự riêng tư của cá nhân.)- Ví dụ: Smart home devices collecting sensitive information could be hacked, leading to misuse or exploitation of private data.
(Những thiết bị gia dụng thông minh sẽ thu thập những thông tin cá nhân nhạy cảm. Những thông tin này có thể bị xâm nhập và rò rỉ bởi kẻ xấu, dẫn tới việc lạm dụng và mua bán thông tin/ dữ liệu cá nhân.)
- Ví dụ: Smart home devices collecting sensitive information could be hacked, leading to misuse or exploitation of private data.
2.2. Bước 2: Lập dàn ý
| Introduction: Viết lại đề bài theo cách khác, sau đó đưa ra quan điểm cá nhân (Bài viết theo hướng negative development) | |
| Body paragraph 1: – Point: Robots lead to the erosion of critical human skills. – Explanation: + Robot handling household chores discourage practicing basic skills like cooking and cleaning. + Workplace robots replace roles requiring critical thinking, manual dexterity, and innovation. – Example: Robotic cooking devices reduce opportunities to learn or improve culinary skills. – Link: Over-reliance on robots weaken autonomy and resilience, leaving society vulnerable to disruptions when technology fails. | |
| Body paragraph 2: – Point: Robots raise substantial concerns about security and privacy – Explanation: + Robots collect sensitive data for operation, which can be exploited if hacked. + Lack of strict data protection regulations worsens the issue. – Examples: + Cleaning robots with cameras can expose home layouts + Workplace robots handling confidential information can cause financial and reputational damage if breached. – Link: Increased robot usage heightens risks of surveillance and cybercrime, undermining trust in technology. | |
| Conclusion: Viết lại mở bài theo cách khác, nhắc lại quan điểm cá nhân. Tóm tắt các main idea đã viết trong các đoạn thân bài. |
2.3. Bước 3: Bài mẫu
2.3.1. Bài mẫu band 5.0+
In today’s world, robots are doing more tasks at home and work. Some people think this is good because it makes life easier, but I believe it is a negative development. This essay will explain why robots cause people to lose skills and create problems with privacy and security.
Robots doing more work can make people lose important skills. At home, robots do things like cooking and cleaning, so people do not learn or practice these tasks anymore. For example, cooking robots that make food automatically mean people do not have to learn how to cook. At work, robots take over jobs that require thinking or special skills. This can make people too dependent on robots, and they will not know what to do if the robots stop working. As a result, people become less independent, and society becomes weaker when technology fails.
Using robots also causes problems with privacy and security. Many robots collect personal data to work properly, but this data can be stolen or misused. For instance, robots that clean houses may have cameras to map the house, and hackers can use this information in bad ways. At work, robots that handle important company data can make mistakes or be hacked, which can cost a company money or damage its reputation. Also, there are not enough rules to protect data, so privacy problems can happen more often. This makes people less safe when they rely on robots too much.
In conclusion, I think using robots for more tasks is a bad idea. It makes people lose skills and creates big risks for privacy and security. We should use robots carefully to make sure they help us without causing harm.
2.3.2. Bài mẫu band 7.5+
In modern society, robots are increasingly taking over tasks at home and in the workplace. While some may view this as a positive development that enhances efficiency and convenience, I firmly believe that this trend is a negative development. This essay will explore the reasons why growing reliance on robots can lead to a loss of essential skills and pose significant security and privacy risks.
Robots performing more tasks can result in the erosion of critical human skills. Firstly, as robots take over household chores, individuals are less inclined to practice basic life skills, such as cooking, cleaning, or even managing finances. For example, robotic cooking devices that prepare meals at the touch of a button discourage people from learning or improving their culinary abilities, leading to a gradual decline in self-reliance. Moreover, in workplaces, robots are replacing humans in roles that require critical thinking, manual dexterity, and innovation. As a result, employees risk becoming over-reliant on technology, leaving them unable to solve problems independently when systems fail. This dependence not only diminishes individual autonomy but also weakens societal resilience in the face of technological malfunctions. A society that lacks essential human skills is more vulnerable to disruptions, which underscores the negative implications of this trend.
The integration of robots into homes and workplaces poses substantial security and privacy concerns. To begin with, many robots, especially smart home devices, rely on collecting sensitive personal data to operate effectively. For instance, cleaning robots equipped with cameras or sensors may store information about the layout of a person’s home, which can be exploited if the system is hacked. Furthermore, in workplaces, robots handling confidential data or monitoring employees can inadvertently expose sensitive information. This can result in not only financial losses but also reputational damage to businesses. In addition, the lack of stringent regulations around data protection in robotics leaves users vulnerable to privacy violations. Consequently, increased robot usage may lead to heightened risks of surveillance and cybercrime, eroding trust in technology. These threats highlight how the growing reliance on robots undermines personal security and privacy, making it a detrimental development.
In conclusion, while robots undeniably bring convenience and efficiency, their increasing role in daily life is, in my view, a negative development. They contribute to the erosion of essential skills, making people overly dependent on technology, and introduce significant security and privacy concerns. It is crucial for individuals and societies to strike a balance between leveraging robotic assistance and preserving essential human capabilities and safety. Only then can we ensure that technology enhances, rather than diminishes, the quality of life.
2.4. Từ vựng
| Từ vựng | Nghĩa |
| Reliance /rɪˈlaɪ.əns/ | (noun) sự phụ thuộc E.g. The reliance on technology has grown significantly in recent years. (Sự phụ thuộc vào công nghệ đã tăng đáng kể trong những năm gần đây.) |
| Erosion /ɪˈroʊ.ʒən/ | (noun) sự thoái hóa E.g. The erosion of trust between the two companies led to the termination of their partnership. (Sự mất dần niềm tin giữa hai công ty đã dẫn đến việc chấm dứt quan hệ đối tác.) |
| Inclined to /ɪnˈklaɪnd tə/ | (adjective phrase) có khuynh hướng E.g. Teenagers may be more inclined to take risks compared to adults. (Thanh thiếu niên có thể có khuynh hướng chấp nhận rủi ro nhiều hơn so với người lớn.) |
| Decline /dɪˈklaɪn/ | (verb) giảm; từ chối E.g. The population of the town has declined significantly in recent years. (Dân số của thị trấn đã giảm đáng kể trong những năm gần đây.) |
| Self-reliance /ˌself.rɪˈlaɪ.əns/ | (noun) sự tự lực, tự chủ E.g. Self-reliance is an important skill for young people to develop. (Tự lực là một kỹ năng quan trọng mà người trẻ cần phát triển.) |
| Manual dexterity /ˈmæn.ju.əl dɛkˈstɛr.ɪ.ti/ | (noun phrase) sự khéo tay E.g. The job requires a high level of manual dexterity to handle delicate components. (Công việc đòi hỏi mức độ khéo tay cao để xử lý các bộ phận tinh vi.) |
| Over-reliant /ˌoʊ.vər.rɪˈlaɪ.ənt/ | (adjective) phụ thuộc quá đáng E.g. He realized he was over-reliant on his parents for financial support. (Anh ấy nhận ra rằng mình đã quá phụ thuộc vào cha mẹ về mặt tài chính.) |
| Diminish /dɪˈmɪn.ɪʃ/ | (verb) giảm bớt, làm suy giảm E.g. Regular exercise can help diminish stress levels significantly. (Tập thể dục thường xuyên có thể giúp giảm đáng kể mức độ căng thẳng.) |
| Individual autonomy /ˌɪn.dəˈvɪdʒ.u.əl əˈtɑː.nə.mi/ | (noun phrase) tự chủ cá nhân E.g. The school encourages individual autonomy by allowing students to choose their own projects. (Trường học khuyến khích sự tự chủ cá nhân bằng cách cho phép học sinh tự chọn dự án của mình.) |
| Societal resilience /səˈsaɪ.ə.təl rɪˈzɪl.jəns/ | (noun phrase) sự bền vững của xã hội E.g. Programs that promote societal resilience often focus on collaboration and community support. (Các chương trình thúc đẩy sự bền vững của xã hội thường tập trung vào sự hợp tác và hỗ trợ cộng đồng.) |
| Technological malfunctions /ˌtek.nəˈlɑː.dʒɪ.kəl ˈmæl.fʌŋk.ʃənz/ | (noun phrase) sự cố công nghệ, trục trặc kỹ thuật E.g. Frequent technological malfunctions delayed the launch of the new product. (Những sự cố công nghệ thường xuyên đã làm trì hoãn việc ra mắt sản phẩm mới.) |
| Disruption /dɪsˈrʌp.ʃən/ | (noun) sự gián đoạn, rối loạn E.g.The pandemic caused widespread disruption in global supply chains. (Đại dịch đã gây ra sự gián đoạn rộng khắp trong chuỗi cung ứng toàn cầu.) |
| Underscore /ˌʌn.dɚˈskɔːr/ | (verb) nhấn mạnh, làm nổi bật E.g. The report underscores the importance of sustainable energy sources. (Báo cáo nhấn mạnh tầm quan trọng của các nguồn năng lượng bền vững.) |
| Integration /ˌɪn.təˈɡreɪ.ʃən/ | (noun) sự hội nhập, tích hợp E.g. Cultural integration plays a crucial role in building a harmonious society. (Hội nhập văn hóa đóng vai trò quan trọng trong việc xây dựng một xã hội hài hòa.) |
| Pose /poʊz/ | (verb) đưa ra, gây ra (vấn đề) E.g. The changes in the policy pose a significant challenge for small businesses. (Những thay đổi trong chính sách gây ra một thách thức lớn cho các doanh nghiệp nhỏ.) |
| Layout /ˈleɪ.aʊt/ | (noun) bố cục, cách sắp xếp, thiết kế E.g. He presented the layout of the new office during the meeting. (Anh ấy đã trình bày bố cục văn phòng mới trong cuộc họp.) |
| Hack /hæk/ | (verb) xâm nhập (máy tính) E.g. Someone tried to hack into the company’s database last night. (Ai đó đã cố gắng xâm nhập vào cơ sở dữ liệu của công ty tối qua.) |
| Confidential data /ˌkɑːn.fəˈden.ʃəl ˈdeɪ.tə/ | (noun phrase) dữ liệu bảo mật, thông tin mật E.g. Leaking confidential data can result in severe legal consequences. (Làm lộ dữ liệu bảo mật có thể dẫn đến những hậu quả pháp lý nghiêm trọng.) |
| Inadvertently /ˌɪn.ədˈvɝː.tənt.li/ | (adverb) một cách vô tình, không cố ý E.g. She inadvertently deleted an important file while organizing her documents. (Cô ấy vô tình xóa một tệp quan trọng khi đang sắp xếp tài liệu.) |
| Sensitive information /ˈsen.sə.tɪv ˌɪn.fɚˈmeɪ.ʃən/ | (noun phrase) thông tin nhạy cảm, dữ liệu nhạy cảm E.g. The document contains sensitive information that should not be disclosed to the public. (Tài liệu này chứa thông tin nhạy cảm không nên công bố ra công chúng.) |
| Stringent /ˈstrɪn.dʒənt/ | (adjective) nghiêm ngặt, khắt khe E.g. Government agencies impose stringent regulations on the disposal of hazardous waste. (Các cơ quan chính phủ áp đặt các quy định nghiêm ngặt về việc xử lý chất thải nguy hại.) |
| Cybercrime /ˈsaɪ.bɚ.kraɪm/ | (noun) tội phạm công nghệ E.g. Cybercrime has become a major concern for businesses worldwide. (Tội phạm mạng đã trở thành một mối lo ngại lớn đối với các doanh nghiệp trên toàn thế giới.) |
| Undeniably /ˌʌn.dɪˈnaɪ.ə.bli/ | (adverb) không thể phủ nhận, rõ ràng E.g. He is undeniably one of the most talented musicians of our generation. (Anh ấy rõ ràng là một trong những nhạc sĩ tài năng nhất của thế hệ chúng ta.) |
| Leverage /ˈliː.vər.ɪdʒ/ | (verb) tận dụng, khai thác E.g. By leveraging technology, we can improve efficiency and reduce costs.(Bằng cách tận dụng công nghệ, chúng ta có thể cải thiện hiệu quả và giảm chi phí.) |
| Culinary abilities /ˈkuː.lɪ.ner.i əˈbɪl.ə.tiz/ | (noun phrase) kỹ năng nấu nướng E.g. Improving your culinary abilities can lead to healthier eating habits. (Cải thiện kỹ năng nấu ăn của bạn có thể dẫn đến thói quen ăn uống lành mạnh hơn.) |
2.5. Cấu trúc
2.5.1. Câu phức sử dụng “as”
| As + [Mệnh đề phụ], [mệnh đề chính] |
E.g. As robots take over household chores, individuals are less inclined to practice basic life skills, such as cooking, cleaning, or even managing finances.
(Khi robot tiếp quản công việc nhà, các cá nhân ít muốn luyện tập những kỹ năng sống cơ bản, như nấu nướng, dọn dẹp, hay ngay cả quản lý tài chính cá nhân.)
- Mệnh đề chính: “Individuals are less inclined to practice basic life skills, such as cooking, cleaning, or even managing finances.”
- Mệnh đề phụ: “As robots take over household chores”
=> Mệnh đề phụ được bắt đầu bằng từ nối phụ thuộc “as”, đóng vai trò làm mệnh đề bổ ngữ, giúp bổ sung thông tin cho mệnh đề chính.
2.5.2. Câu phức với mệnh đề danh từ
| S1 + V1 + O2 + [mệnh đề danh từ] |
E.g. This essay will explore the reasons why growing reliance on robots can lead to a loss of essential skills and pose significant security and privacy risks.
(Bài luận này sẽ tìm hiểu các lý do tại sao sự phụ thuộc ngày càng tăng vào robot có thể dẫn đến mất đi các kỹ năng thiết yếu và gây ra những rủi ro đáng kể về an ninh và quyền riêng tư.)
- Mệnh đề chính: “This essay will explore the reasons”
- Mệnh đề danh từ: “Why growing reliance on robots can lead to a loss of essential skills and pose significant security and privacy risks.”
=> Mệnh đề danh từ giúp giải thích cho tân ngữ “the reasons” trong mệnh đề chính.
2.5.3. Câu đơn với đồng vị ngữ
| S + [appositive phrase] + V + O |
E.g. To begin with, many robots, especially smart home devices, rely on collecting sensitive personal data to operate effectively.
(Trước hết, nhiều robot, đặc biệt là các thiết bị nhà thông minh, dựa vào việc thu thập dữ liệu cá nhân nhạy cảm để hoạt động hiệu quả.)
- Mệnh đề chính: “Many robots rely on collecting sensitive personal data to operate effectively.”
- Cụm trạng từ: “To begin with,”
- Cụm đồng vị ngữ: “ especially smart home devices”
=> Cụm trạng từ đóng vai trò giới thiệu câu, tạo ra một sự chuyển tiếp giữa câu trước với câu này.
=> Cụm đồng vị ngữ đóng vai trò bổ ngữ cho chủ ngữ “many robots”, giúp thêm thông tin cụ thể cho chủ ngữ.
3. Kết luận
Việc nắm vững cách làm và ôn luyện kỹ từng dạng bài trong IELTS Writing là chìa khóa giúp bạn tự tin hơn và đạt được kết quả cao nhất. Thông qua bài giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 28/12/2024, mình mong rằng bạn sẽ nắm vững các chiến lược hiệu quả để làm bài thi, đồng thời cải thiện kỹ năng viết cho các dạng bài mà bạn có thể gặp trong tương lai.
Nếu có bất kỳ câu hỏi hoặc thắc mắc nào, bạn đừng ngần ngại để lại bình luận bên dưới. Đội ngũ biên tập của Vietop English luôn sẵn sàng đồng hành và hỗ trợ bạn một cách tận tình và nhanh chóng.
Chúc bạn đạt kết quả cao trong kỳ thi IELTS sắp tới!

![[ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 27/01/2026](https://vietop.edu.vn/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/thumbnail-giai-de-ielts-writing-ngay-27-01-2026.jpg)

![[ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 07/04/2025](https://vietop.edu.vn/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/giai-de-ielts-writing-ngay-07-04-2025.png)

![[ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 15/03/2025](https://vietop.edu.vn/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/giai-de-ielts-writing-ngay-15-03-2025.jpg)
![[ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 22/03/2025](https://vietop.edu.vn/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/giai-de-ielts-writing-ngay-22-03-2025.jpg)
![[ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 08/03/2025](https://vietop.edu.vn/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/giai-de-ielts-writing-ngay-08-03-2025.jpg)
![[ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 06/03/2025](https://vietop.edu.vn/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/giai-de-ielts-writing-ngay-06-03-2025.jpg)
