Vào ngày 05/12/2024, các thí sinh tham dự kỳ thi IELTS đã trải qua bài thi IELTS Writing với dạng bài Bar Chart và dạng Advantages-Disadvantages. Theo mình, hai dạng đề này cùng chủ đề thi có độ khó ở mức trung bình.
Trong bài viết này, mình sẽ cùng bạn phân tích chi tiết, giải đề và đưa ra những gợi ý hữu ích để bạn có thể tiếp cận và xử lý đề bài một cách hiệu quả nhất. Trước tiên, hãy cùng mình xem qua đề bài cụ thể:
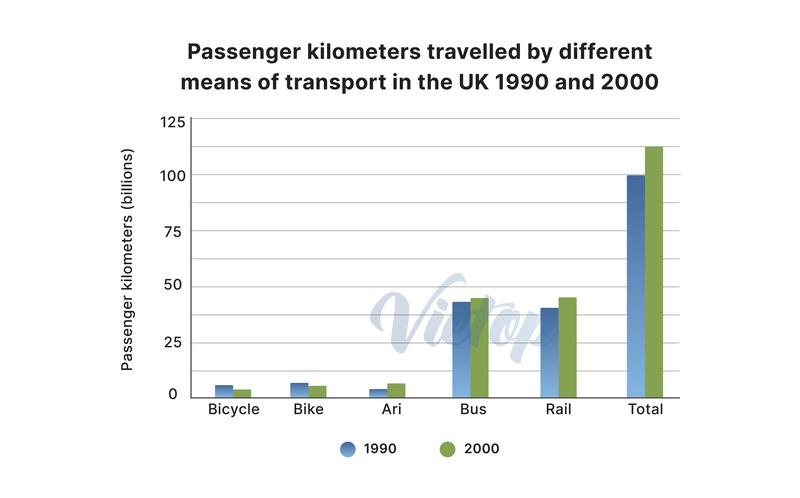
- Đề IELTS Writing Task 1: The chart shows the total distance traveled by passengers on five types of transport in the UK between 1990 and 2000.
- Đề IELTS Writing Task 2: In some countries, there has been an increase in the number of parents who educate their children themselves at home instead of sending them to school. Do you think the advantages of this outweigh the disadvantages?
Cùng theo dõi bài giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 05/12/2024 với các bài mẫu band 5.0+ và 7.5+. Cùng mình học bài thôi!
1. IELTS Writing Task 1
| The chart shows the total distance travelled by passengers on five types of transport in the UK between 1990 and 2000. |
| (Biểu đồ cho thấy tổng quãng đường mà hành khách đã di chuyển bằng năm loại phương tiện giao thông ở Vương quốc Anh trong giai đoạn từ năm 1990 đến năm 2000.) |
1.1. Bước 1: Phân tích đề
- Dạng biểu đồ: Biểu đồ cột (bar chart)
- Topic: Tổng số kilomet hành khách đã đi bằng 5 phương tiện khác nhau ở Vương quốc Anh vào năm 1990 và năm 2000
- Number of factors: 6
- Time: Năm 1990 và năm 2000
- Tense: Các thì quá khứ
- Nhóm dữ liệu: 3 nhóm dữ liệu => 3 đoạn thân bài
- Nhóm các phương tiện ít được sử dụng: Bicycle, Bike, Airplane
- Nhóm các phương tiện được sử dụng nhiều: Bus, Rail
- Tổng số kilomet của tất cả các phương tiện (optional)
1.2. Bước 2: Lập dàn ý
Introduction: Paraphrase đề bài.
Overview:
- The total distance travelled by all modes increased significantly.
- Buses and trains saw the highest usage.
- Bicycles, motorbikes, and air travel had much lower figures.
| Body paragraph 1: Các phương tiện ít được sử dụng | Body paragraph 2: Các phương tiện được sử dụng nhiều |
| – Bicycle: Around 5 billion kilometers in both years with no significant change. – Bike (motorbike): Also stable at around 5 billion kilometers. – Air Travel: Slight increase from 5 billion kilometers in 1990 to 8 billion kilometers in 2000. | – Bus: Increased from around 45 billion kilometers in 1990 to nearly 50 billion kilometers in 2000. – Rail: Rose from 40 billion kilometers in 1990 to 45 billion kilometers in 2000. |
| Body paragraph 3: Tổng số kilomet của tất cả các phương tiện (optional) – The total distance traveled by all forms of transport combined rose from around 100 billion kilometers in 1990 to over 120 billion kilometers in 2000 | |
Xem thêm:
- Cách viết IELTS Writing Task 1 từ A – Z
- Cách viết dạng Diagram (Process) IELTS Writing Task 1
- Cách viết dạng Maps IELTS Writing Task 1
1.3. Bước 3: Bài mẫu
1.3.1. Bài mẫu band 5.0+
The chart shows how far passengers traveled by five types of transport in the UK in 1990 and 2000. The transport types are bicycle, bike, air, bus, and rail.
Overall, the total distance traveled was higher in 2000 than in 1990. Buses and trains had the most distance, while bicycles, bikes, and air travel had much smaller numbers.
In 1990 and 2000, bicycles and bikes had low numbers. They both stayed around 5 billion kilometers. Air travel was also low, but it went up a little to about 8 billion kilometers in 2000.
For buses and trains, the numbers were much higher. Buses were the highest with about 45 billion kilometers in 1990 and a bit more in 2000. Trains were also high, going up from 40 billion to 45 billion kilometers.
1.3.2. Bài mẫu band 7.5+
The chart illustrates the total distance traveled by passengers using five types of transport in the UK in 1990 and 2000. The modes of transport include bicycles, motorbikes, air travel, buses, and trains, with figures shown in billions of passenger kilometers.
Overall, the total distance traveled by all means of transport increased significantly over the decade. While buses and trains saw considerable use compared to other modes, air travel, bicycles, and motorbikes remained the least used forms of transport.
In terms of low-usage modes, bicycles and motorbikes showed minimal passenger kilometers, each accounting for around 5 billion kilometers in both 1990 and 2000, with barely any change. Air travel, though still low compared to other modes, experienced a slight increase, rising from around 5 billion kilometers in 1990 to approximately 8 billion kilometers in 2000.
On the other hand, high-usage modes like buses and trains demonstrated significantly higher distances. Buses were the most popular mode of transport, rising from about 45 billion kilometers in 1990 to nearly 50 billion in 2000. Rail travel also increased slightly, from approximately 40 billion kilometers in 1990 to about 45 billion kilometers in 2000.
The total distance traveled by all forms of transport combined rose from around 100 billion kilometers in 1990 to over 120 billion kilometers in 2000.
1.4. Từ vựng
| Từ vựng | Nghĩa |
| Means of transport /miːnz əv ˈtrænspɔːrt/ | (noun phrase) phương tiện giao thông E.g. Public buses and trains are common means of transport in urban areas. (Xe buýt công cộng và xe lửa là những phương tiện giao thông phổ biến ở khu vực thành thị.) |
| Remain /rɪˈmeɪn/ | (verb) vẫn còn, duy trì, ở lại E.g. Despite the heavy rain, many people remained at the event. (Mặc dù trời mưa lớn, nhiều người vẫn ở lại sự kiện.) |
| Minimal /ˈmɪnɪməl/ | (adjective) tối thiểu, rất nhỏ E.g. The project was completed with minimal resources. (Dự án được hoàn thành với nguồn lực tối thiểu.) |
| Account for /əˈkaʊnt fɔːr/ | (phrasal verb) giải thích, chiếm (một phần), chịu trách nhiệm E.g. Women account for 50% of the workforce in the company. (Phụ nữ chiếm 50% lực lượng lao động trong công ty.) |
| Barely /ˈbeə(r)li/ | (adverb) hầu như không, chỉ vừa đủ E.g. He could barely see the road through the heavy fog. (Anh ấy hầu như không nhìn thấy đường qua lớp sương mù dày đặc.) |
| Significantly /sɪɡˈnɪfɪkəntli/ | (adverb) đáng kể, một cách quan trọng E.g. The company’s profits have increased significantly this year. (Lợi nhuận của công ty đã tăng lên đáng kể trong năm nay.) |
| Approximately /əˈprɒksɪmətli/ | (adverb) khoảng chừng, xấp xỉ E.g. The journey takes approximately two hours by car. (Chuyến đi mất khoảng chừng hai tiếng nếu đi bằng xe hơi.) |
1.5. Cấu trúc
1.5.1. Câu phức với mệnh đề trạng ngữ và cụm phân từ
| S, [mệnh đề trạng ngữ], V + O1, V_ing + O2 |
E.g. Air travel, though still low compared to other modes, experienced a slight increase, rising from around 5 billion kilometers in 1990 to approximately 8 billion kilometers in 2000.
(Vận tải hàng không, mặc dù vẫn còn thấp so với các phương thức khác, đã có sự gia tăng nhẹ, tăng từ khoảng 5 tỷ km vào năm 1990 lên khoảng 8 tỷ km vào năm 2000.)
=> Câu phức với chủ ngữ chính là “Air travel”, có mệnh đề trạng ngữ chỉ sự tương phản “though still low compared to other modes” giúp bổ nghĩa cho việc “experienced a slight increase” của chủ ngữ. Cụm phân từ “rising from….” giúp bổ sung thông tin cho mệnh đề chính “Air travel experienced a slight increase”.
1.5.2. Câu phức với từ nối “while”
| While + S1 + V1, S2 + V2 |
E.g. While buses and trains saw considerable use compared to other modes, air travel, bicycles, and motorbikes remained the least used forms of transport.
(Trong khi xe buýt và tàu hỏa được sử dụng đáng kể so với các phương tiện khác, vận tải hàng không, xe đạp và xe máy vẫn là những hình thức vận chuyển ít được sử dụng nhất.)
=> Câu phức sử dụng “while” ở đầu câu để giới thiệu mệnh đề phụ thuộc “buses and trains saw considerable use compared to other modes” đóng vai trò đưa ra thông tin tương phản với mệnh đề chính “air travel, bicycles, and motorbikes remained the least used forms of transport”.
Xem thêm:
- [ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 30/11/2024
- [ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 23/11/2024
- [ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 16/11/2024
- Tổng hợp đề thi IELTS Writing 2024 kèm bài mẫu chi tiết
2. IELTS Writing Task 2
| In some countries, there has been an increase in the number of parents who educate their children themselves at home instead of sending them to school. Do you think the advantages of this outweigh the disadvantages? |
| (Ở một số quốc gia, đã có sự gia tăng về số lượng phụ huynh tự giáo dục con cái tại nhà thay vì cho con đi học ở trường. Bạn có nghĩ rằng những lợi ích của việc này vượt trội hơn những bất lợi không?) |
2.1. Bước 1: Phân tích đề
- Dạng bài: Advantages – Disadvantages
- Từ khóa: Increase, number of parents, educate their children themselves at home, instead of, sending them to school, advantages, outweigh, disadvantages.
- Phân tích yêu cầu: Đề yêu cầu bạn đưa ra ý kiến xem lợi ích của việc cha mẹ tự dạy con ở nhà thay vì cho con đi học ở trường có nhiều hơn bất lợi của nó hay không.
=> Dạng bài Advantages – Disadvantages có “outweigh”, nên mình có các cách viết như sau:
- Cách 1: Advantages > disadvantages: Mình sẽ đưa ra 2 advantages, mỗi advantage 1 đoạn, sau đó dành 1 đoạn bàn về disadvantages, nhưng đoạn này sẽ lập luận bác bỏ/ giảm độ mạnh của disadvantages xuống => thân bài có 3 đoạn.
- Cách 2: Disadvantages > advantages: Mình sẽ đưa ra 2 disadvantages, mỗi disadvantage 1 đoạn, sau đó dành 1 đoạn bàn về advantages, nhưng đoạn này sẽ lập luận bác bỏ/ giảm độ mạnh của advantages xuống => thân bài có 3 đoạn.
Trong bài mẫu này, mình sẽ viết theo hướng disadvantages > advantages
2.2. Bước 2: Lập dàn ý
| Introduction: Viết lại đề bài theo cách khác, sau đó đưa ra quan điểm cá nhân. (disadvantages > advantages) | |
| Body paragraph 1: Disadvantage 1 – Main point: One major drawback of homeschooling is the lack of social interaction. + Supporting idea 1: Traditional schools allow children to develop teamwork, communication skills, and friendships. + Supporting idea 2: Homeschooled children may struggle to work in groups or adapt to social settings later in life. + Link: This isolation can hinder social and emotional development | |
| Body paragraph 2: Disadvantage 2 – Main point: Another significant disadvantage of homeschooling is the lack of formal accreditation. + Supporting idea 1: Parents may lack the qualifications to teach effectively, and homeschool curricula are often not recognized by official institutions. + Supporting idea 2: Homeschooled students might face challenges when applying to universities or jobs due to non-standardized assessments. + Link: This can limit future educational and career opportunities. | |
| Body paragraph 3: Advantages – Point: While homeschooling does offer some benefits, such as a safer environment and stronger family bonds, these are less significant compared to the disadvantages. + Explanation: Homeschooling can protect children from bullying and foster close relationships => However, these benefits do not make up for the lack of social and academic development. + Link: The stress on parents and the limited resources at home often reduce the effectiveness of these advantages. | |
| Conclusion: Viết lại mở bài theo cách khác, nhắc lại quan điểm cá nhân. Tóm tắt các main idea đã viết trong các đoạn thân bài. |
2.3. Bước 3: Bài mẫu
2.3.1. Bài mẫu band 5.0+
In recent years, more parents have decided to teach their children at home instead of sending them to regular schools. While this choice has some benefits, like a safer environment and closer family relationships, the disadvantages are more serious. The biggest problems are that children do not get to socialize much and may not receive proper qualifications for their future.
One big problem with homeschooling is that children do not get enough social interaction. In regular schools, kids learn to make friends, work in groups, and improve their communication. These skills are important for their growth and confidence. When children study at home, they can feel lonely and left out. Later in life, they may find it difficult to work with others or join group activities.
Another major disadvantage is that homeschooled children may not get the right kind of education. Parents are not always trained to teach, so they may miss important topics or teach in the wrong way. Also, many homeschool programs are not officially accepted by colleges. This makes it hard for students to get into universities or find good jobs in the future. For example, a student may do well at home but still struggle to apply to college because their education is not recognized.
It is true that homeschooling can protect children from bullying and bad influences at school. It also allows families to spend more time together. However, these benefits do not make up for the problems of homeschooling. Teaching children at home can be stressful for parents, and this may affect how well they teach.
In conclusion, homeschooling has some good points, like safety and family time, but the problems are more serious. Children need social interaction and a proper education to succeed. For most families, regular schools give a better education and help children prepare for the future.
2.3.2. Bài mẫu band 7.5+
In recent years, an increasing number of parents in some countries have opted to educate their children at home rather than enrolling them in traditional schools. Although homeschooling offers benefits such as a safer learning environment and closer family bonds, these advantages are often overshadowed by significant drawbacks. The lack of socialization and formal accreditation can have long-lasting negative effects on a child’s development and future prospects.
One major drawback of homeschooling is the limited opportunity for socialization. In traditional schools, children experience a structured environment where they can interact with peers, develop teamwork skills, and build lasting friendships. These experiences are essential for their emotional and social growth. In contrast, homeschooled children may become isolated from their age group. This isolation can hinder their ability to adapt to a group setting later in life. For instance, when they enter collaborative work environments as adults, they might struggle with communication or feel out of place.
Another critical disadvantage is the absence of formal accreditation. Many parents, despite their dedication, are not trained educators. This can result in gaps in knowledge or ineffective teaching methods. Furthermore, some homeschooling curricula are not recognized by official educational institutions. As a result, students may face difficulties with college admission or future employment. For example, a homeschooled student may perform well in specific subjects but lack the credentials required for competitive university programs due to non-standardized assessments.
It is true that homeschooling can provide a safer learning environment, shielding children from peer pressure and bullying. However, this advantage does not compensate for the broader educational and social experiences found in traditional schools. Family bonds may also be fostered through homeschooling, yet the responsibility of teaching can place a tremendous burden on parents. Juggling multiple duties can lead to burnout, which may result in a less effective learning experience for the child.
In conclusion, while homeschooling offers some positive aspects, such as a secure learning environment and stronger family bonds, the drawbacks outweigh these benefits. The lack of socialization and formal accreditation can have serious consequences for a child’s development and opportunities. For most children, the comprehensive education, teamwork skills, and recognized qualifications provided by traditional schools make them a superior option.
Xem thêm:
- Cách viết mở bài Writing Task 2
- Cách viết Problem and Solution trong IELTS Writing Task 2
- Cách làm dạng bài IELTS Writing Task 2 – Agree or Disagree
2.4. Từ vựng
| Từ vựng | Nghĩa |
| Enroll /ɪnˈrəʊl/ | (verb) ghi danh, đăng ký E.g. Many students choose to enroll in online courses for flexibility. (Nhiều học viên chọn đăng ký các khóa học trực tuyến vì sự linh hoạt.) |
| Learning environment /ˈlɜːnɪŋ ɪnˈvaɪrənmənt/ | (noun phrase) môi trường học tập E.g. A positive learning environment helps students stay motivated and engaged. (Một môi trường học tập tích cực giúp học sinh luôn có động lực và tập trung.) |
| Overshadow /ˌoʊvərˈʃædoʊ/ | (verb) làm lu mờ, che khuất, át đi E.g. His achievements were overshadowed by his brother’s success. (Thành tựu của anh ấy bị làm lu mờ bởi thành công của anh trai.) |
| Socialization /ˌsoʊʃəlaɪˈzeɪʃn/ | (noun) sự hòa nhập xã hội E.g. Early childhood education plays a crucial role in children’s socialization. (Giáo dục mầm non đóng vai trò quan trọng trong sự hòa nhập xã hội của trẻ em.) |
| Formal accreditation /ˈfɔːrml əˌkrɛdɪˈteɪʃn/ | (noun phrase) sự công nhận chính thức, sự kiểm định chính thức E.g. Many employers require candidates to have formal accreditation from recognized institutions. (Nhiều nhà tuyển dụng yêu cầu ứng viên phải có sự công nhận chính thức từ các tổ chức được công nhận.) |
| Homeschooling /ˈhoʊmˌskuːlɪŋ/ | (noun) giáo dục tại nhà, học tại nhà E.g. Homeschooling allows parents to tailor the curriculum to their child’s needs. (Giáo dục tại nhà cho phép phụ huynh điều chỉnh chương trình học phù hợp với nhu cầu của con mình.) |
| Peer /pɪər/ | (noun) bạn đồng trang lứa, người ngang hàng E.g. Children often learn important social skills by interacting with their peers. (Trẻ em thường học các kỹ năng xã hội quan trọng khi tương tác với bạn đồng trang lứa.) |
| Isolate /ˈaɪsəleɪt/ | (verb) cô lập, cách ly E.g. Some parents worry that homeschooling might isolate their children from social interactions. (Một số phụ huynh lo lắng rằng giáo dục tại nhà có thể cô lập con cái họ khỏi các tương tác xã hội.) |
| Collaborative work /kəˈlæbərətɪv wɜːrk/ | (noun phrase) công việc hợp tác, làm việc nhóm E.g. Collaborative work helps students develop communication and teamwork skills. (Làm việc nhóm giúp học sinh phát triển kỹ năng giao tiếp và làm việc nhóm.) |
| Trained educator /treɪnd ˈɛdʒəkeɪtər/ | (noun phrase) giáo viên có chuyên môn E.g. A trained educator can effectively address different learning styles in the classroom. (Một giáo viên có chuyên môn có thể đáp ứng hiệu quả các phong cách học tập khác nhau trong lớp học.) |
| Educational institution /ˌɛdʒuˈkeɪʃənl ˌɪnstɪˈtjuːʃn/ | (noun phrase) cơ sở giáo dục, tổ chức giáo dục E.g. Many students aim to attend a prestigious educational institution for higher studies. (Nhiều học sinh mong muốn theo học tại một cơ sở giáo dục danh tiếng để học lên cao.) |
| College admission /ˈkɒlɪdʒ ədˈmɪʃən/ | (noun phrase) tuyển sinh đại học, nhập học đại học E.g. High grades and extracurricular activities can improve your chances of college admission. (Điểm số cao và các hoạt động ngoại khóa có thể cải thiện cơ hội nhập học đại học của bạn.) |
| Non-standardized assessment /nɒn-ˈstændədaɪzd əˈsɛsmənt/ | (noun phrase) đánh giá phi tiêu chuẩn, đánh giá không theo tiêu chuẩn E.g. Non-standardized assessments allow for more flexibility in measuring a student’s progress. (Đánh giá phi tiêu chuẩn cho phép linh hoạt hơn trong việc đo lường tiến bộ của học sinh.) |
| Peer pressure /pɪər ˈprɛʃər/ | (noun phrase) áp lực từ bạn bè, áp lực đồng trang lứa E.g. Many teenagers face peer pressure to fit in with their friends. (Nhiều thanh thiếu niên chịu áp lực từ bạn bè để hòa nhập với bạn bè của mình.) |
| Burnout /ˈbɜːrnaʊt/ | (noun) sự kiệt sức, tình trạng kiệt quệ E.g. Working long hours without breaks can lead to burnout. (Làm việc nhiều giờ mà không nghỉ ngơi có thể dẫn đến sự kiệt sức.) |
| Comprehensive /ˌkɒmprɪˈhɛnsɪv/ | (adjective) toàn diện, bao quát E.g. The course offers a comprehensive overview of modern economics. (Khóa học cung cấp một cái nhìn toàn diện về kinh tế học hiện đại.) |
| Teamwork skills /ˈtiːmwɜːrk skɪlz/ | (noun phrase) kỹ năng làm việc nhóm E.g. Group projects are a great way to develop teamwork skills. (Các dự án nhóm là cách tuyệt vời để phát triển kỹ năng làm việc nhóm.) |
| Furthermore /ˌfɜːrðərˈmɔːr/ | (adverb) hơn nữa, ngoài ra E.g. The project was successful. Furthermore, it was completed ahead of schedule. (Dự án đã thành công. Hơn nữa, nó còn được hoàn thành trước thời hạn.) |
| Group setting /ɡruːp ˈsɛtɪŋ/ | (noun phrase) môi trường nhóm E.g. Working in a group setting helps students develop communication skills. (Làm việc trong môi trường nhóm giúp học sinh phát triển kỹ năng giao tiếp.) |
| Foster /ˈfɔːstər/ | (verb) nuôi dưỡng, thúc đẩy, bồi dưỡng E.g. Teachers should aim to foster a love for learning in their students. (Giáo viên nên cố gắng nuôi dưỡng tình yêu học tập ở học sinh.) |
| Family bond /ˈfæmɪli bɒnd/ | (noun phrase) mối liên kết gia đình, tình cảm gia đình E.g. Spending quality time together strengthens the family bond. (Dành thời gian chất lượng bên nhau giúp củng cố mối liên kết gia đình.) |
2.5. Cấu trúc
2.5.1. Câu ghép với yet
| S1 + V1, yet + S2 + V2 |
E.g. Family bonds may also be fostered through homeschooling, yet the responsibility of teaching can place a tremendous burden on parents.
(Mối liên kết gia đình cũng có thể được nuôi dưỡng thông qua việc giáo dục tại nhà, tuy nhiên trách nhiệm giảng dạy có thể đặt một gánh nặng lớn lên vai phụ huynh.)
=> Câu ghép với mệnh đề độc lập “Family bonds may also be fostered through homeschooling” với từ nối “yet” được sử dụng để giới thiệu mệnh đề độc lập tiếp theo có ý nghĩa ám chỉ sự tương phản với mệnh đề trước “the responsibility of teaching can place a tremendous burden on parents.”
2.5.2. Câu phức sử dụng mệnh đề danh từ và cụm phân từ
| S + V + C + [mệnh đề danh từ] + V-ing + N |
E.g. It is true that homeschooling can provide a safer learning environment, shielding children from peer pressure and bullying.
(Sự thật là giáo dục tại nhà có thể mang lại một môi trường học tập an toàn hơn, bảo vệ trẻ em khỏi áp lực từ bạn bè và nạn bắt nạt.)
=> Câu phức với mệnh đề chính là “It is true”, mệnh đề danh từ “that homeschooling can provide a safer learning environment” đóng vai trò bổ nghĩa cho chủ ngữ “it”, và cụm phân từ “shielding children from peer pressure and bullying” bổ sung thêm thông tin cho mệnh đề danh từ.
2.5.3. Câu đơn sử dụng cụm danh từ ghép làm chủ ngữ và cụm giới từ
| [Prepositional phrase] + S + V + O |
E.g. For most children, the comprehensive education, teamwork skills, and recognized qualifications provided by traditional schools make them a superior option.
(Đối với hầu hết trẻ em, nền giáo dục toàn diện, kỹ năng làm việc nhóm và các chứng chỉ được công nhận mà trường học truyền thống cung cấp khiến chúng trở thành một lựa chọn ưu việt.)
=> Câu đơn sử dụng cụm giới từ “For most children” giúp cung cấp ngữ cảnh cho câu, cụm danh từ ghép “the comprehensive education, teamwork skills, and recognized qualifications provided by traditional schools” làm chủ ngữ, liệt kê ra những lợi ích của trường học truyền thống, thể hiện được sự thành thạo về mặt ngữ pháp.
3. Kết luận
Việc chuẩn bị kỹ lưỡng cho từng dạng đề trong IELTS Writing là chìa khóa giúp bạn tự tin và đạt điểm số như mong đợi. Qua bài phân tích và giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 05/12/2024, mình hy vọng rằng bạn đã nắm được những chiến lược hiệu quả để xử lý đề bài, từ đó cải thiện đáng kể kỹ năng viết của bản thân.
Nếu bạn còn bất kỳ câu hỏi hay thắc mắc nào, đừng ngần ngại để lại bình luận. Đội ngũ biên tập viên của Vietop English sẽ luôn đồng hành và hỗ trợ bạn tận tình.
Chúc các bạn ôn tập tốt và đạt được kết quả cao trong kỳ thi IELTS sắp tới!

![[ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 27/01/2026](https://vietop.edu.vn/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/thumbnail-giai-de-ielts-writing-ngay-27-01-2026.jpg)

![[ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 07/04/2025](https://vietop.edu.vn/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/giai-de-ielts-writing-ngay-07-04-2025.png)

![[ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 15/03/2025](https://vietop.edu.vn/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/giai-de-ielts-writing-ngay-15-03-2025.jpg)
![[ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 22/03/2025](https://vietop.edu.vn/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/giai-de-ielts-writing-ngay-22-03-2025.jpg)
![[ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 08/03/2025](https://vietop.edu.vn/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/giai-de-ielts-writing-ngay-08-03-2025.jpg)
![[ACE THE TEST] Giải đề IELTS Writing ngày 06/03/2025](https://vietop.edu.vn/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/giai-de-ielts-writing-ngay-06-03-2025.jpg)
