Chemistry – hóa học được cho là chủ đề khá khó trong cả IELTS Speaking và Writing, khi đa số thí sinh không có nhiều kiến thức về hóa học cũng như từ vựng cho chủ đề này. Với bài viết dưới đây, Vietop English mời các bạn cùng tham khảo phần tổng hợp IELTS Vocabulary in Chemistry – Từ vựng IELTS Speaking và Writing chủ đề Chemistry thông dụng.
Từ vựng IELTS Speaking & Writing chủ đề Chemistry – Danh từ
| Từ vựng | Ý nghĩa | Ví dụ |
| Acid | Axit | Vinegar is an example of an acid, which has a sour taste and reacts with metals. |
| Alloy | Hợp kim | Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, which is commonly used for musical instruments. |
| Atom | Nguyên tử | An atom is the basic unit of a chemical element, consisting of a nucleus and electrons. |
| Base | Bazơ | A base is a substance that can accept hydrogen ions and can be found in cleaning products and antacids. |
| Biochemistry | Hóa sinh | Biochemistry is the study of the chemical processes within living organisms. |
| Bond | Liên kết | A chemical bond is a force that holds atoms together in molecules, such as in the bond between hydrogen and oxygen in water. |
| Carbon | Carbon | Carbon is a chemical element that is the basis for all known life on Earth. |
| Catalyst | Chất xúc tác | A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. |
| Chemical | Hóa chất | A chemical is a substance made up of atoms or molecules, which can undergo chemical reactions. |
| Compound | Hợp chất | A compound is a substance made up of two or more elements that are chemically bonded together, such as water. |
| Crystal | Pha lê | A crystal is a solid material with a regular repeating pattern of atoms, such as salt crystals. |
| Density | Tỉ trọng | Density is a measure of the amount of mass contained in a given volume of a substance. |
| Element | Yếu tố | An element is a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means, such as oxygen. |
| Enzyme | Enzym | An enzyme is a protein that catalyzes chemical reactions in living organisms. |
| Gas | Khí ga | A gas is a state of matter that has no fixed shape or volume, such as oxygen. |
| Hydrocarbon | Hiđrocacbon | A hydrocarbon is a molecule made up of hydrogen and carbon atoms, such as methane. |
| Inorganic | Vô cơ | Inorganic compounds are those that do not contain carbon, such as salts. |
| Ion | Ion | An ion is an atom or molecule with an electrical charge, such as sodium ions. |
| Isotope | Đồng vị | An isotope is a version of an element with a different number of neutrons in the nucleus, such as carbon-14. |
| Kinetics | Động học | Kinetics is the study of the rates of chemical reactions. |
| Matter | Vật chất | Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space, such as solids, liquids, and gases. |
| Molecule | Phân tử | A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are chemically bonded together, such as oxygen gas. |
| Neutralization | Trung hòa | Neutralization is a chemical reaction between an acid and a base that results in the formation of salt and water. |
| Nitrogen | Nitơ | Nitrogen is a chemical element that is a key component of many important molecules, such as DNA. |
| Organic | Hữu cơ | Organic compounds are those that contain carbon, such as sugars and proteins. |
Xem ngay:
IELTS Vocabulary in Cosmology – Astrophysics
Cách phát âm ed trong tiếng Anh chuẩn nhất
IELTS Vocabulary topic Veterinary science và Ornithology
IELTS Vocabulary in Logic – Từ vựng chủ đề Logic trong tiếng Anh
Từ vựng IELTS Speaking & Writing chủ đề Chemistry – Động từ
| Từ vựng | Ý nghĩa | Ví dụ |
| Analyze | Phân tích | The scientist analyzed the sample to determine its chemical composition. |
| Calculate | Tính toán | We need to calculate the amount of reagent required for the experiment. |
| Combine | Kết hợp | The two elements can be combined to form a new compound. |
| Convert | Chuyển thành | We need to convert the units of measurement to compare the results. |
| Decompose | Phân hủy | The organic matter decomposes and releases carbon dioxide. |
| Detect | Phát hiện | The instrument can detect even the smallest amounts of impurities. |
| Dissolve | Hòa tan | The solute dissolves in the solvent to form a solution. |
| Evaporate | Bay hơi | The liquid will evaporate if left in an open container. |
| Experiment | Cuộc thí nghiệm | The students conducted an experiment to test their hypothesis. |
| Filter | Lọc | We need to filter the solution to remove any solids. |
| Identify | Nhận dạng | The test will help to identify the presence of a particular chemical. |
| Measure | Đo lường | We need to measure the temperature of the reaction. |
| Mix | Pha trộn | The two solutions can be mixed to form a homogeneous mixture. |
| Neutralize | Trung hòa | The acid can be neutralized by adding a base. |
| Observe | Quan sát | The scientist observed the reaction to study its kinetics. |
| Precipitate | Kết tủa | The addition of a reagent caused a precipitate to form. |
| React | Phản ứng | The two chemicals react to form a new compound. |
| Separate | Chia | The components of the mixture can be separated using a distillation apparatus. |
| Synthesize | Tổng hợp | The chemist synthesized a new molecule with unique properties. |
| Test | Phép thử | The test can determine the acidity of a solution. |
| Titrate | Chuẩn độ | The solution needs to be titrated to determine its concentration. |
| Vaporize | Bốc hơi | The liquid will vaporize when heated to a certain temperature. |
| Volatilize | Bay hơi | The compound will volatilize when exposed to air. |
| Weigh | Cân | We need to weigh the sample before adding it to the reaction. |
| Yield | Năng suất | The reaction yielded a high amount of product. |
Xem thêm:
Từ vựng tiếng Anh về Trường học
Từ vựng IELTS Listening theo chủ đề
Từ vựng giới thiệu bản thân trong tiếng Anh và các mẫu câu thông dụng
Từ vựng IELTS Speaking & Writing chủ đề Chemistry – Tính từ

| Từ vựng | Ý nghĩa | Ví dụ |
| Acidic | Có tính axit | The ph of the solution is highly acidic. |
| Alkaline | Kiềm | The soil is alkaline and unsuitable for certain plants. |
| Aqueous | Nước | The compound is highly soluble in aqueous solutions. |
| Basic | Nền tảng | Sodium hydroxide is a basic compound. |
| Chemical | Hóa chất | The chemical reaction produced a new compound. |
| Concentrated | Tập trung, tập hợp | The concentrated solution is highly reactive. |
| Corrosive | Ăn mòn | The acid is highly corrosive and must be handled with care. |
| Crystalline | Kết tinh | The compound forms beautiful, crystalline structures. |
| Flammable | Dễ cháy | The liquid is highly flammable and must be stored carefully. |
| Gaseous | Khí | The element is normally found in a gaseous state. |
| Hazardous | Nguy hiểm | The chemical is considered hazardous and requires special handling. |
| Hydrophobic | Kị nước | The molecule is hydrophobic and does not dissolve in water. |
| Inert | Trơ | The gas is inert and does not react with other substances. |
| Ionic | Ion | The compound is formed by the attraction between oppositely charged ionic species. |
| Molecular | Phân tử | The molecule has a complex, three-dimensional structure. |
| Organic | Hữu cơ | The compound contains carbon atoms and is considered organic. |
| Oxidised | Bị oxy hóa | The metal has been oxidised and has formed a rust layer. |
| pH | ph | The ph of the solution indicates its acidity or basicity. |
| Radioactive | Phóng xạ | The material is highly radioactive and must be handled with great care. |
| Redox | Oxi hóa khử | The reaction involves a redox process, where one species is oxidized and another is reduced. |
| Saturated | Bão hòa | The solution is saturated with solute and cannot dissolve any more. |
| Soluble | Hòa tan | The compound is highly soluble in water. |
| Toxic | Độc hại | The chemical is toxic and can cause harm if ingested or inhaled. |
| Unstable | Không ổn định | The compound is unstable and decomposes quickly. |
| Volatile | Bay hơi | The compound is highly volatile and evaporates easily. |

Hơn 21.220+ học viên đã đạt chứng chỉ tiếng Anh quốc tế, tự tin giao tiếp và mở rộng cơ hội học tập – nghề nghiệp. Đăng ký ngay để không bỏ lỡ cơ hội!
Từ vựng IELTS Speaking & Writing chủ đề Chemistry – Trạng từ
| Từ vựng | Ý nghĩa | Ví dụ |
| Accurately | Chính xác | The volume was measured accurately using a calibrated pipette. |
| Actively | Tích cực | The enzyme actively catalyzes the reaction. |
| Catalytically | Xúc tác | The reaction proceeds catalytically in the presence of a catalyst. |
| Chemically | Về mặt hóa học | The compound reacts chemically with oxygen to form a new product. |
| Concentrically | Đồng tâm | The circles were drawn concentrically to represent different reaction conditions. |
| Efficiently | Hiệu quả | The reaction was carried out efficiently using a novel catalyst. |
| Exothermically | Tỏa nhiệt | The reaction proceeds exothermically, releasing heat. |
| Experimentally | Thực nghiệm | The kinetic parameters were determined experimentally using a series of experiments. |
| Homogeneously | Đồng nhất | The reagents were mixed homogeneously to ensure uniform reaction conditions. |
| Inorganically | Vô cơ | The compound is inorganically synthesized using a variety of methods. |
| Kinetically | Động học | The reaction rate was studied kinetically to determine the rate law. |
| Mechanically | Máy móc | The compound was synthesized mechanically using a ball mill. |
| Nonpolarly | Không phân cực | The molecule interacts nonpolarly with the solvent. |
| Precisely | Đúng | The temperature was controlled precisely using a temperature controller. |
| Rapidly | Liên tục | The reaction proceeds rapidly in the presence of a strong acid. |
| Selectively | Có chọn lọc | The catalyst selectively promotes one reaction pathway over others. |
| Slowly | Chậm | The reaction proceeds slowly in the absence of a catalyst. |
| Spontaneously | Tự phát | The reaction proceeds spontaneously without the need for external energy input. |
| Stereoselectively | Chọn lọc lập thể | The reaction proceeds stereoselectively, favouring one stereoisomer over others. |
| Stereospecifically | Có sự bố trí cố định trong không gian | The reaction proceeds stereospecifically, forming only one stereoisomer. |
| Stoichiometrically | Cân bằng hóa học | The reagents were added stoichiometrically to ensure a complete reaction. |
| Synthetically | Tổng hợp | The compound was synthesized synthetically using a stepwise approach. |
| Thermodynamically | Nhiệt động học | The reaction was studied thermodynamically to determine its equilibrium constant. |
| Transesterification | Phản ứng trao đổi giữa rượu và este | The reaction involves the transesterification of one ester to another. |
| Unimolecularly | Đơn phân tử | The reaction proceeds unimolecular, involving only one reactant. |
>>> Xem thêm:
Các nguyên tố hóa học tiếng Anh thông dụng
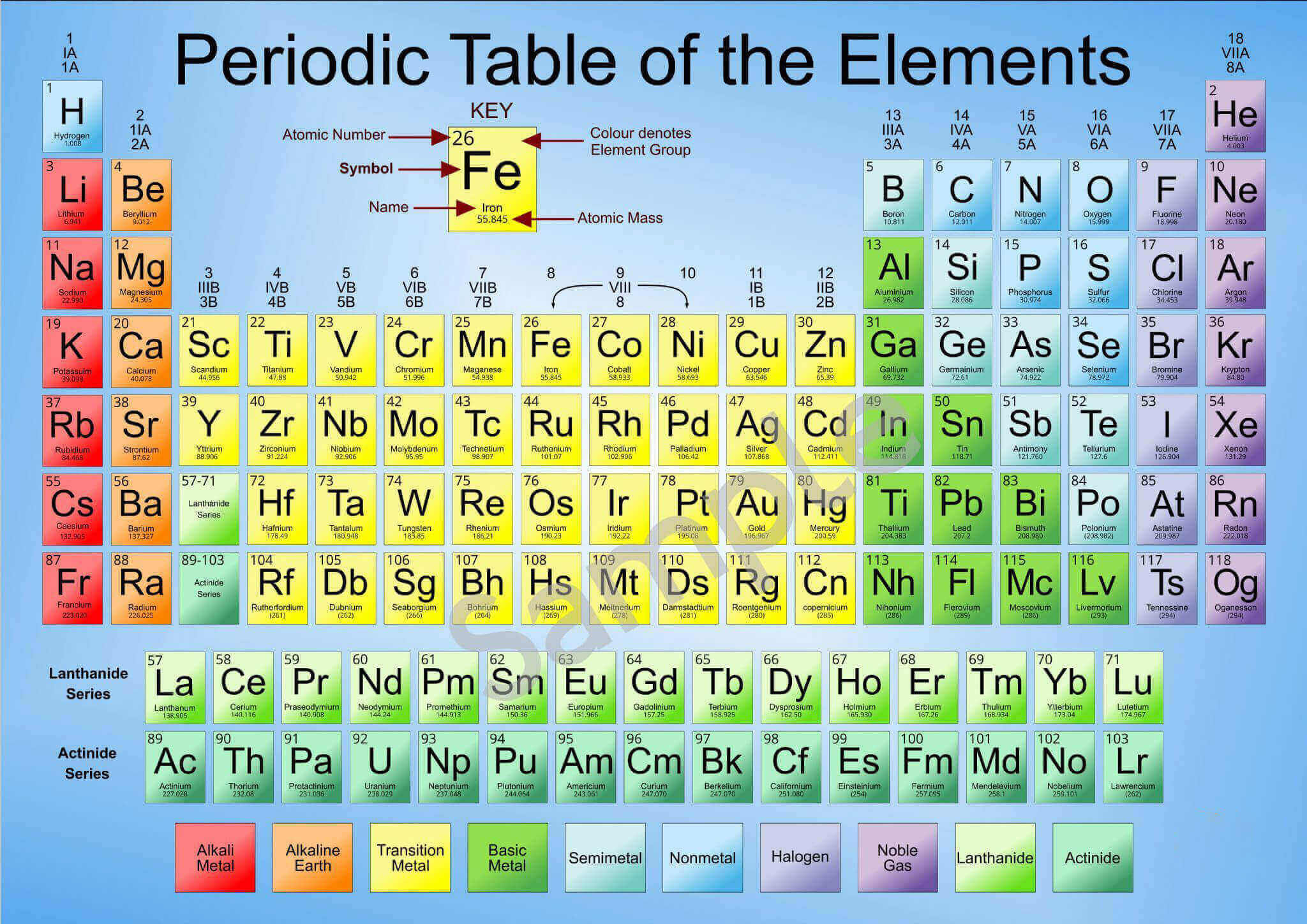
| Các nguyên tố hóa học tiếng Anh | Nghĩa |
| Aluminum (Al) | Nhôm (Al) |
| Argon (Ar) | Argon (Ar) |
| Arsenic (As) | Asen (As) |
| Beryllium (Be) | Berili (Be) |
| Boron (B) | Bo (B) |
| Bromine (Br) | Nước brom (Br) |
| Cadmium (Cd) | Cadmi (Cd) |
| Calcium (Ca) | Canxi (Ca) |
| Carbon (C) | Cacbon (C) |
| Chlorine (Cl) | Clo (Cl) |
| Chromium (Cr) | Crom (Cr) |
| Cobalt (Co) | Coban (Co) |
| Copper (Cu) | Đồng (Cu) |
| Fluorine (F) | Flo (F) |
| Gallium (Ga) | Gali (Ga) |
| Germanium (Ge) | Gecmani (Ge) |
| Helium (He) | Heli (Anh) |
| Hydrogen (H) | Hydro (H) |
| Indium (In) | Indi (Trong) |
| Iron (Fe) | Sắt (Fe) |
| Krypton (Kr) | Krypton (Kr) |
| Lithium (Li) | Liti (Lý) |
| Magnesium (Mg) | Magiê (Mg) |
| Manganese (Mn) | Mangan (Mn) |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | Molypden (Mo) |
| Neon (Ne) | Neon (Nê) |
| Nickel (Ni) | Niken (Ni) |
| Niobium (Nb) | Niobi (Nb) |
| Nitrogen (N) | Nitơ (N) |
| Oxygen (O) | Oxy (O) |
| Palladium (Pd) | Palađi (Pd) |
| Phosphorus (P) | Phốt pho (P) |
| Potassium (K) | Kali (K) |
| Rhodium (Rh) | Rhodi (Rh) |
| Rubidium (Rb) | Rubidi (Rb) |
| Ruthenium (Ru) | Rutheni (Ru) |
| Scandium (Sc) | Scandi (Sc) |
| Selenium (Se) | Selen (Se) |
| Silicon (Si) | Silic (Si) |
| Silver (Ag) | Bạc (Ag) |
| Sodium (Na) | Natri (Na) |
| Strontium (Sr) | Stronti (Sr) |
| Sulfur (S) | Lưu huỳnh (S) |
| Technetium (Tc) | Tecneti (Tc) |
| Tin (Sn) | Thiếc (Sn) |
| Titanium (Ti) | Titan (Ti) |
| Vanadium (V) | Vanadi (V) |
| Yttrium (Y) | Yttri (Y) |
| Zinc (Zn) | Kẽm (Zn) |
| Zirconium (Zr) | Zirconi (Zr) |
Xem ngay: Khóa học IELTS Cấp tốc – Cam kết tăng ít nhất 0.5 – 1.0 band score SAU 1 THÁNG HỌC
Các thuật ngữ tiếng Anh chủ đề hóa học thông dụng
| Các nguyên tố hóa học tiếng Anh | Nghĩa |
| Acid | Axit |
| Amorphous solid | Chất rắn vô định hình |
| Atom | Nguyên tử |
| Base | Ba-zơ |
| Battery | Ắc quy |
| Biochemistry | Hóa sinh |
| Boyle’s law | Định luật Boyle |
| Catalyst | Chất xúc tác |
| Charles’s law | Định luật Charles |
| Chemical bond | Liên kết hóa học |
| Chemical equation | Phương trình hóa học |
| Chemical equilibrium | Cân bằng hóa học |
| Chemical reaction | Phản ứng hóa học |
| Compound | Hợp chất |
| Concentration | Sự tập trung |
| Covalent bond | Liên kết cộng hóa trị |
| Crystal structure | Cấu trúc tinh thể |
| Diffusion | Khuếch tán |
| Electrochemical cell | Tế bào điện hóa |
| Electrolysis | Điện phân |
| Element | Yếu tố |
| Enthalpy | Entanpi |
| Entropy | Sự hỗn loạn |
| Fuel cell | Pin nhiên liệu |
| Galvanic cell | Tế bào điện |
| Gas laws | Luật khí |
| Gay-Lussac’s law | Định luật Gay-Lussac |
| Heat capacity | Nhiệt dung |
| Hydrogen bond | Liên kết hydro |
| Ideal gas law | Luật khí lý tưởng |
| Inorganic chemistry | Hóa học vô cơ |
| Ion | Ion |
| Ionic bond | Sự gắn kết |
| Isotope | Đồng vị |
| Molecule | Phân tử |
| Monomer | Monome |
| Organic chemistry | Hóa học hữu cơ |
| Osmosis | Thẩm thấu |
| Oxidation | Quá trình oxy hóa |
| Periodic table | Bảng tuần hoàn |
| pH | Độ pH |
| Phase diagram | Giản đồ pha |
| Polymer | Polyme |
| Polymerization | Trùng hợp |
| Redox reaction | Phản ứng oxi hỏa khứ |
| Reduction | Sự giảm bớt |
| Solid-state chemistry | Hóa học trạng thái rắn |
| Solubility | Độ hòa tan |
| Subatomic particles | Các hạt hạ nguyên tử |
| Thermodynamics | Nhiệt động học |
Thuật ngữ và viết tắt trong tiếng Anh chuyên ngành hóa học

| Thuật ngữ và viết tắt chuyên ngành | Ý nghĩa |
| AC – Alternating current | Dòng điện xoay chiều |
| DC – Direct current | Dòng điện một chiều |
| UV – Ultraviolet | Tia cực tím |
| IR – Infrared | Hồng ngoại |
| NMR – Nuclear magnetic resonance | Cộng hưởng từ hạt nhân |
| MS – Mass spectrometry | Khối phổ |
| TLC – Thin-layer chromatography | Sắc ký lớp mỏng |
| GC – Gas chromatography | Sắc ký khí |
| HPLC – High-performance liquid chromatography | Sắc ký lỏng hiệu năng cao |
| FTIR – Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy | Quang phổ hồng ngoại biến đổi Fourier |
| SEM – Scanning electron microscopy | Kính hiển vi điện tử quét |
| TEM – Transmission electron microscopy | Kính hiển vi điện tử truyền qua |
| XRD – X-ray diffraction | Nhiễu xạ tia X |
| XRF – X-ray fluorescence | Huỳnh quang tia X |
| Raman – Raman spectroscopy | Quang phổ Raman |
| EPR – Electron paramagnetic resonance | Cộng hưởng thuận từ điện tử |
| AFM – Atomic force microscopy | Kính hiển vi lực nguyên tử |
| STM – Scanning tunneling microscopy | Kính hiển vi quét đường hầm |
| EDX – Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy | Quang phổ tia X tán sắc năng lượng |
| ICP-MS – Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry | Khối phổ plasma kết hợp tự cảm |
| PCR – Polymerase chain reaction | Phản ứng chuỗi polymerase |
| ELISA – Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay | Xét nghiệm hấp thụ miễn dịch liên kết với enzyme |
| SDS-PAGE – Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis | Điện di gel natri dodecyl sulfat polyacrylamide |
| MALDI-TOF – Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight | Thời gian bay của laser được hỗ trợ bởi ma trận |
| ATR – Attenuated total reflectance | Tổng phản xạ suy giảm |
| DSC – Differential scanning calorimetry | Phép đo nhiệt lượng quét vi sai |
| TGA – Thermogravimetric analysis | Phân tích nhiệt lượng |
| DMA – Dynamic mechanical analysis | Phân tích cơ học động |
| HNMR – Proton nuclear magnetic resonance | Cộng hưởng từ hạt nhân proton |
| CNMR – Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance | Cộng hưởng từ hạt nhân Carbon-13 |
| ESI-MS – Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry | Khối phổ ion hóa Electrospray |
| AAS – Atomic absorption spectroscopy | Quang phổ hấp thụ nguyên tử |
| AES – Atomic emission spectroscopy | Quang phổ phát xạ nguyên tử |
| ICP-OES – Inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy | Quang phổ phát xạ quang plasma cảm ứng |
| FID – Flame ionization detector | Đầu dò ion hóa ngọn lửa |
| PID – Photoionization detector | Máy dò quang hóa |
| GC-MS – Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry | Sắc ký khí khối phổ |
| ICP-AES – Inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy | Quang phổ phát xạ nguyên tử plasma liên kết cảm ứng |
| XAS – X-ray absorption spectroscopy | Quang phổ hấp thụ tia X |
| XPS – X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy | Quang phổ quang điện tử tia X |
| ESCA – Electron spectroscopy for chemical analysis | Quang phổ điện tử để phân tích hóa học |
| MALDI – Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization | Giải hấp/ion hóa laser có hỗ trợ ma trận |
| LDI – Laser desorption ionization | Ion hóa giải hấp bằng laser |
| THF – Tetrahydrofuran | Tetrahydrofuran |
| DMSO – Dimethyl sulfoxide | Dimetyl sulfoxit |
| DMF – Dimethylformamide | Dimetylformamit |
| NMP – N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone | N-Metyl-2-pyrrolidon |
| TMS – Tetramethylsilane | Tetrametylsilan |
| TEA – Triethylamine | Triethylamine |
Trên đây là bài viết tổng hợp IELTS Vocabulary in Chemistry thông dụng, hy vọng các bạn đã có thể tham khảo thêm được nhiều từ vựng hay để không còn thấy khó khăn khi gặp chủ đề này. Vietop English chúc các bạn học tốt và hẹn các bạn ở những bài viết sau nhé!









